Electronic Speech Systems (ESS)
Electronic Speech Systems (ESS)
Electronic Speech Systems (ESS) started in 1989, and are most famous for their AudioDrive chips, used in many sound cards.
 Most AudioDrive chips are Sound Blaster Pro-compatible. All cards post-ES688 got the very good sounding integrated FM synthesizer circuits called "ESFM". These were OPL3-compatible but developed in-house, and has 20 voices, 72 operators, and operated in two modes: Native and Legacy. In Native mode, ESFM allows more than six 4-operator FM voices to be mapped, potentially allowing for a significant increase in the complexity of tones generated. The drivers for Windows 9x incorporate their own custom instrument patches which make use of this extended Native mode. Conversely, Legacy mode provides full backward-compatibility with Yamaha's YMF262. ESFM's output in this mode is moderately faithful to the YMF262 overall, but some tones are rendered quite differently, resulting in unique distortions in the sound and music of some games. Many DOS gamers prefer the softer sound of the ESFM implementation over Yamaha's original OPL3 output.
Most AudioDrive chips are Sound Blaster Pro-compatible. All cards post-ES688 got the very good sounding integrated FM synthesizer circuits called "ESFM". These were OPL3-compatible but developed in-house, and has 20 voices, 72 operators, and operated in two modes: Native and Legacy. In Native mode, ESFM allows more than six 4-operator FM voices to be mapped, potentially allowing for a significant increase in the complexity of tones generated. The drivers for Windows 9x incorporate their own custom instrument patches which make use of this extended Native mode. Conversely, Legacy mode provides full backward-compatibility with Yamaha's YMF262. ESFM's output in this mode is moderately faithful to the YMF262 overall, but some tones are rendered quite differently, resulting in unique distortions in the sound and music of some games. Many DOS gamers prefer the softer sound of the ESFM implementation over Yamaha's original OPL3 output.
Lots of games had specific support for ESS sound cards.
All cards with ESS chips prior to the ES1688 require the loading of a TSR called ENMPU.EXE to enable the MPU-401 interface (if you require external MIDI).
In 1995, ESS launched the first all-in-one 16-bit audio chipset, ES1688. This same year they announced the ES1868 audio chipset, ES968 interface chip, and followed soon after with the ES938 Audio Effects Processor. They also released two wavetable chips, ES689 and ES690F. The company had seen dramatic growth, with $3.7 million in the first quarter of 1994 to $21.4 million in 2Q 1995, and jumping to $31.4 million in 3Q 1995.
In January 1996, ESS announced their acquisition of VideoCore Technology, Inc. for 525,000 shares of common stock and $6.0 million in cash. VideoCore were an advanced compression technology IC manufacturer for digital video products. One month later, they acquired OSEE Technologies, Inc., a developer of fax/modem technology.
This same year, Yamaha filed a patent infringement lawsuit surrounding ESS' ESFM technology. Yamaha had sued ESS Technology, Inc. for infringing two patents which Yamaha claimed covered aspects of FM synthesis technology. Yamaha requested the U.S. District Court to prohibit ESS Technology, Inc.'s sales of products using this technology, but the District Court refused, ruling that Yamaha's chances of prevailing at trial were " ... at best weak.". They settled in May 1996, though the details of the settlement were kept sealed.
In October 1996, ESS introduced three new chips to their AudioDrive range: ES1869, ES1887 and ES1879. The ES1869 was a slightly upgraded version of the ES1868, adding 48 kHz sample playback as well as 3D spatial audio. The ES1887, despite the name, was a slightly upgraded version of the ES1888 and added improved configurability for Windows Plug and Play, and the ES1879 was their new mobile (embedded) offering with an onboard ES938 3D effects processor from Spatializer, and allowed connectivity to an ES689 or ES69x wavetable
1997 saw the introduction of ESS' PCI AudioDrive range. Some PCI-interface AudioDrives, namely the ES1938 Solo-1 and ES1946 Solo-1E, also provided legacy DOS compatibility through Distributed DMA, the SB-Link interface, and ESS' own Transparent DMA (TDMA). This was a necessary requirement for cards to achieve PC98 compliance. TDMA creates a virtual ISA bus and forms a bridge between it and the PCI bus. Note that despite ESS claiming Windows Sound System compatibility on some of their chips (Solo-1, Maestros, etc.), this was only true due to their provision of a 16-bit Windows driver - these cards will not run in WSS mode in DOS.
In 1998 the start of the second-generation of PCI chipsets from ESS arrived, namely the ES1948/1968/1978 Maestro and ES1988/ES1989 Allegro series, all with 3D positional audio capability from QSound and Sensaura.
Numerous games have explicit support for "ESS AudioDrive", sometimes referred to as "ESS Enhanced". Note that this usually refers to models ESS688 and ESS1688 only.
Here are some tools and drivers for ESS chips that are not necessarily model-specific:
- Windows 9x drivers v4.04.00.1327 for cards ES688, ES1488, ES1688, ES1788, ES1868, ES1869, ES1878, ES1879, ES1888 and ES1898.
- MPU-401-compatible MIDI device driver
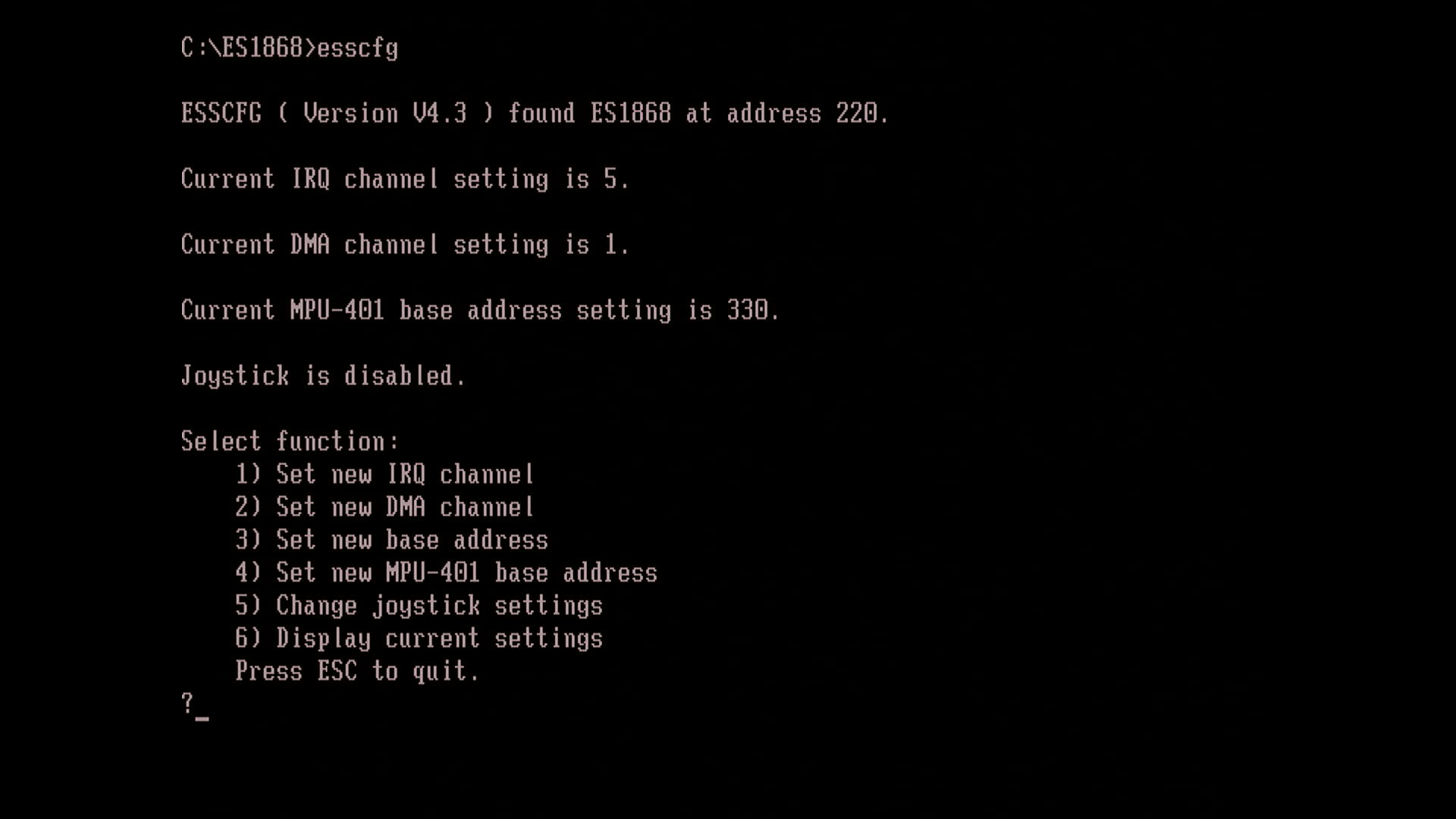
- ESS DOS Config
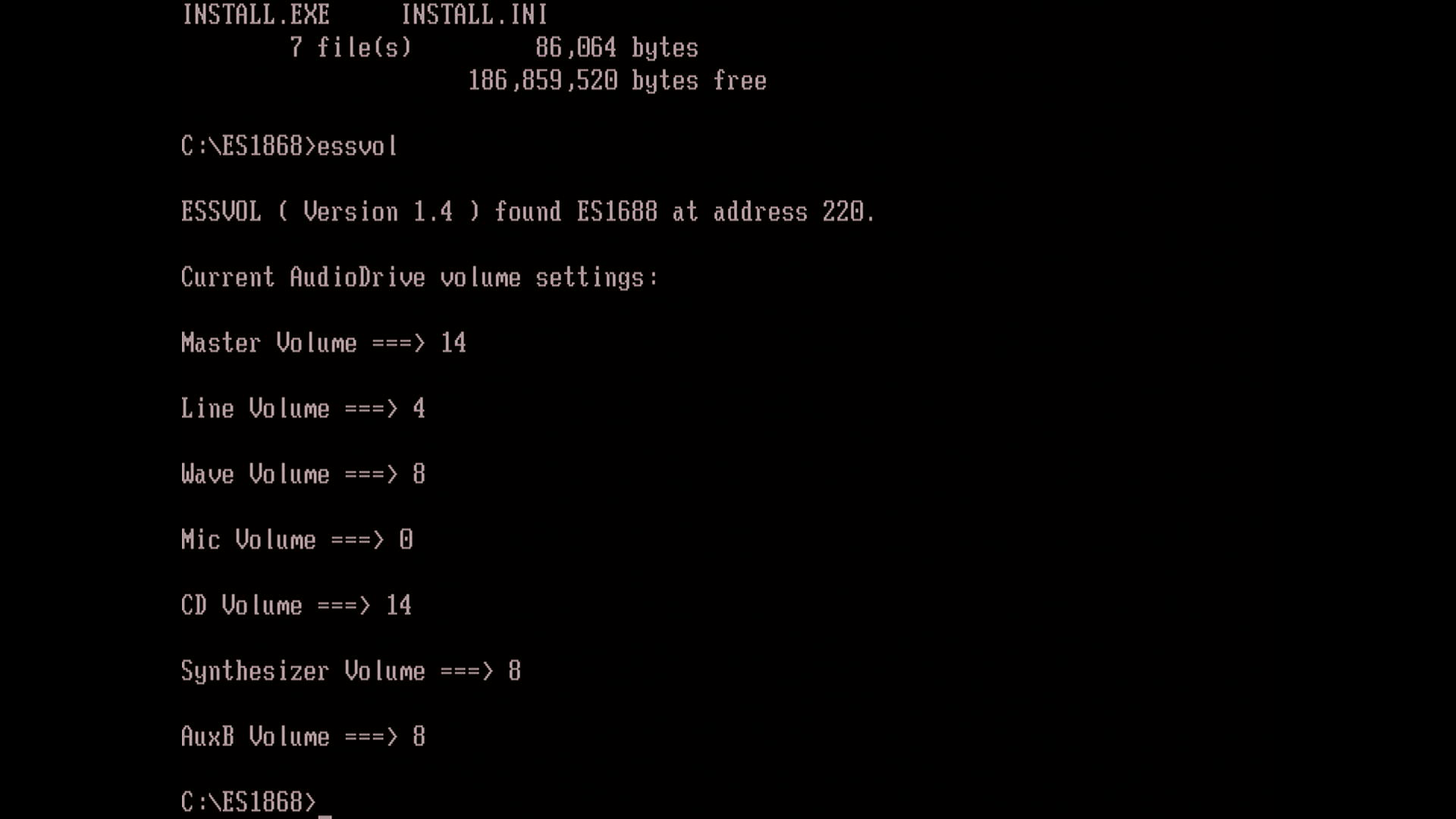
The DOS utility ESSCFG.EXE is used to initialise the card and then it exits (it doesn't remain in memory which is good). ESSVOL.EXE can be used to set the volume levels including those for MIDI and CD Audio.
ESS Chipsets at a glance:
| Description | ES488 | ES688 | ES1488 | ES1688 | ES1698 | ES1788 | ES1888 | ES1887 | ES1868 | ES1869 ES1898 |
ES1878 ES978 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESFM™ | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Mixing Channels (Playback / Record) |
0 | 5/5 | 5/5 | 6/5 | 6/5? | 6/5 | 7/6 | 7/7 | 6/6 | 6/6 | 7/5 |
| Wavetable Serial Port | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Full / Half Duplex | Half | Half | Half | Half | Half | Half | Full | Full | Full | Full | Full |
| Hardware Mixing Accelerator | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Advanced Power Management | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Hardware Volume Control | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Plug and Play Support | M/B | M/B | M/B | M/B | ISA | ISA | N/B | ||||
| Joystick Timers | external | external | external | external | external | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3D Stereo Sound Effect Integrated | X(?) | X | X | ||||||||
| I2S Interface for Zoom Video Port | X | X | |||||||||
| Hot-dock Interface to Expansion Mixer | X |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
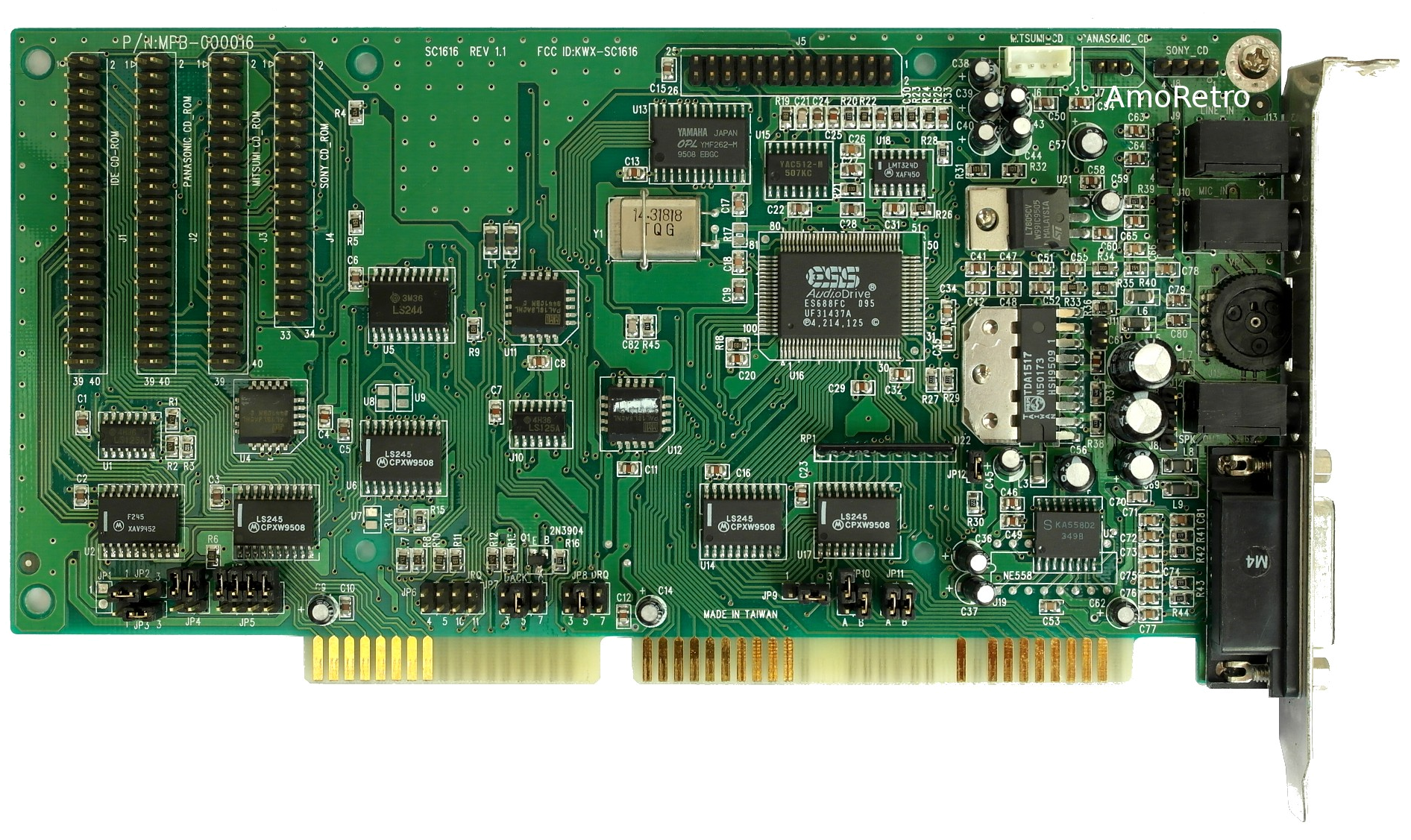
ES688 AudioDrive
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
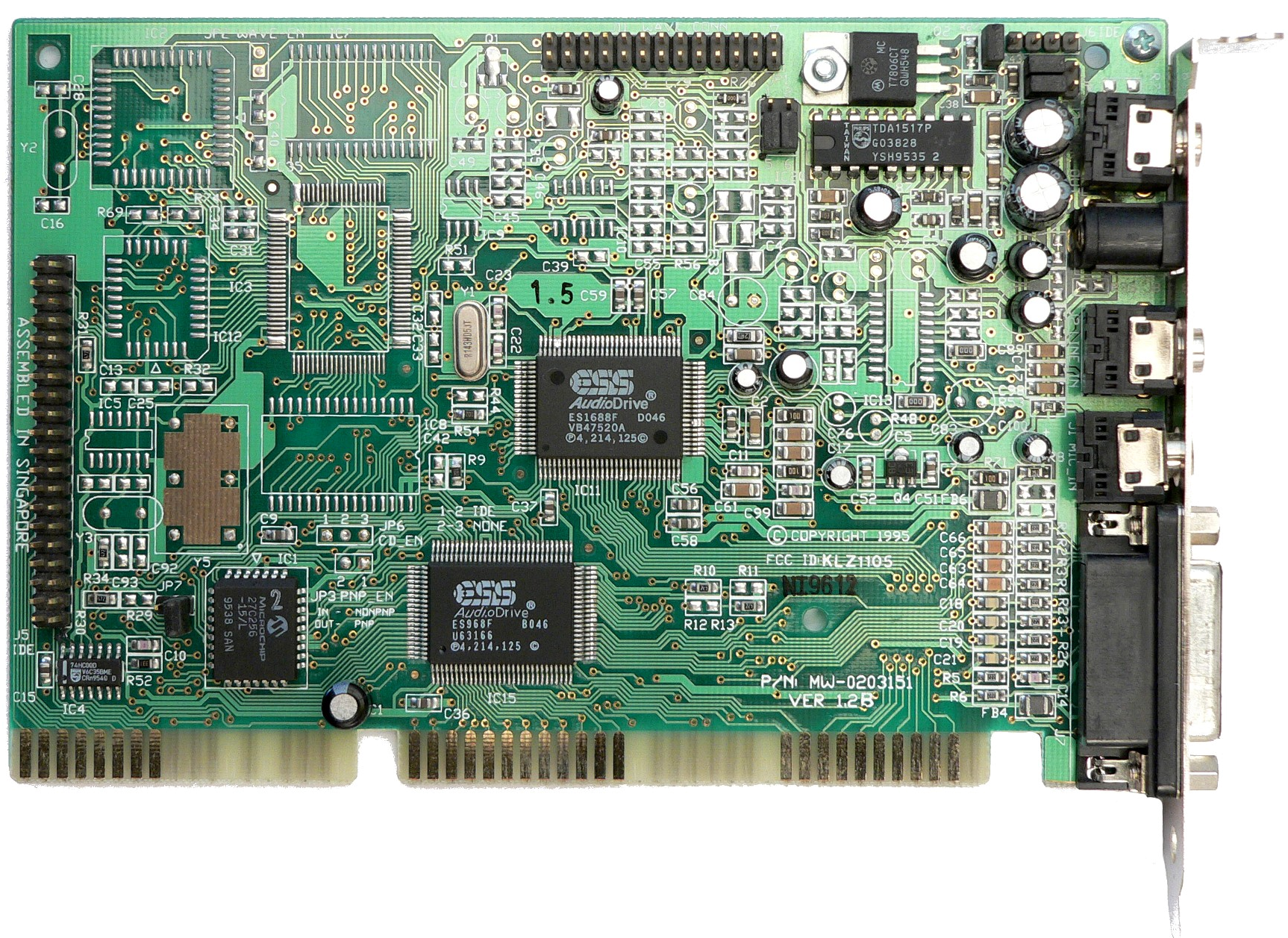
ES1688 AudioDrive
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ES1868 AudioDrive
|
More Images
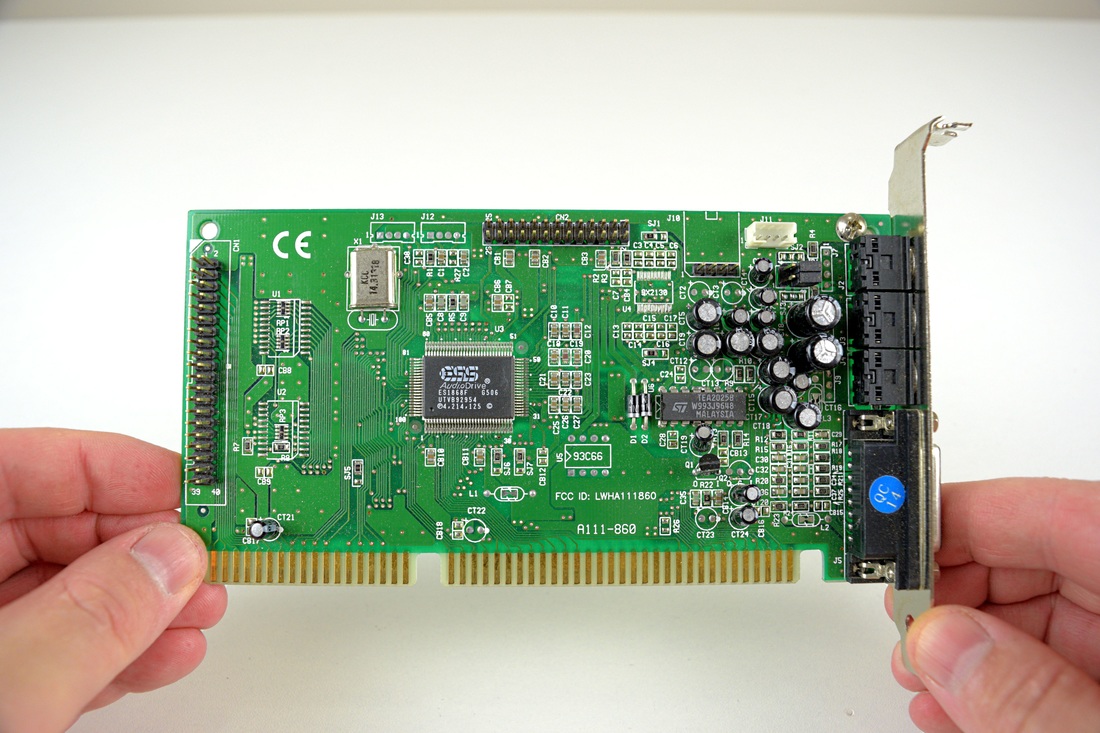
ES1868 Binaura 3D 





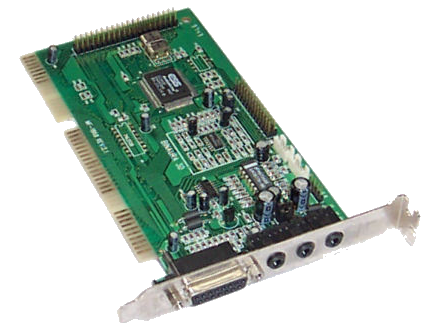
Released in 1997
Interface: 16-bit ISA
Chipset: ES1868
Full Duplex 16-bit Stereo 44.1kHz
Sound Blaster / Sound Blaster Pro compatible
FM Synthesizer ESS ESFM (Yamaha OPL3 compatible) .
Hardware MPU-401 UART interface.
Plug & Play.
"BINAURA 3D" sound.
Built-in stereo amplifier LM1817.
WaveTable connector
IDE CD-ROM Interface
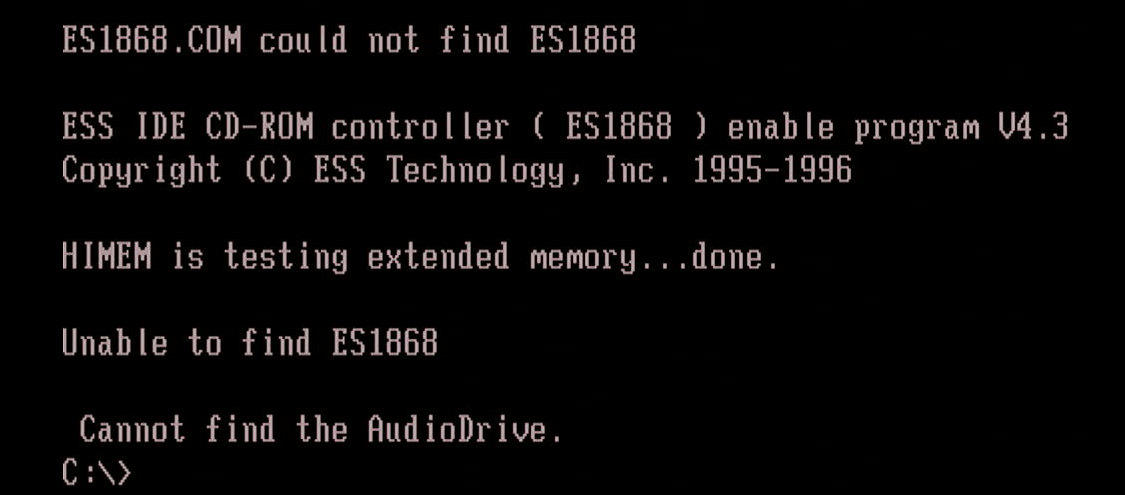
The ES1868 card is low-noise card that supports up to SB Pro 2.0 gaming, considered one of the best DOS gaming cards. It has an IDE header onboard as well as a wavetable header which does not suffer from any bugs like SB card hanging notes bug.
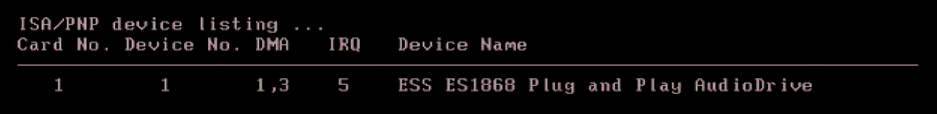
If used with a PnP BIOS, the command-line options for ESSCFG utility are ignored.
The IDE interface can be configured to run at I/O address 168h or 1E8h, and use IRQ 10, 11 or 12.
You can set the onboard jumpers to disable the onboard amplifier and you will get pretty decent output from this card. Suitable for 99% of DOS games.
Drivers: DOS Windows 3.1, NT 3.51, NT 4.0, Windows 95, Windows 98, OS/2 Warp
Here are some notes from ESS on their Spatializing technology:
Everyone knows what stereo sound is. But how the brain perceives it, is important in order to better understand 3D sound. For example, if a piano sound is played through just the left speaker then we will perceive the sound as coming from the left side. If the same sound (and same level, or volume, of sound) is also passed through the right speaker then it will create the effect of the piano sound coming from the center of the two speakers - in essence from a "phantom" speaker. By manipulating the levels of the audio signals to the left & right speakers, and then adding 'effects' to them, it is possible to create up to two extra "phantom" speakers - thus giving us 3D Sound. Further to this we must then understand two more '3D terminologies' - Sum and Difference...
Sum describes the information of each monophonic audio signal sent to the left & right speakers (in other words - the sound, and to which speaker). Difference is the information we have when we look at the left & right signals in terms of level, timing/delay and frequency. By subtracting the Difference of the right signal from the Difference of the left signal we come out with the all-important 'spatial' information which characterizes stereo program material - and it is this which can be manipulated to produce 3D sound. It is important to note that for the best 3D results you should not add any effect to the Sum signal because this would affect the tone of the sound and result in lost tonal quality, and poor audio quality. This is where other 3D technologies fail. Instead 3D Spatializer concentrates purely on the Difference signal. These Difference signals are passed through a psychoacoustically correct filter which performs three critical functions. First it boosts the portion of the audio spectrum which we rely on most for spatial localization cues. Secondly it adds just enough phase delay, and further delays different parts of the Difference signal so that the sense of "space" and size of the "sweet-spot" is dramatically increased. Finally it has a filter/delay block which will prevent acoustic cancellation at low frequencies, so avoiding a sense of weak bass response. Another area of improvement over its competitors is that 3D Spatializer monitors the incoming signals, and if it senses existing spatial information it will only process this to it's optimum performance level. This is because 3D technology is now often used in the recording and game industry, and as such there is a danger of "over-processing" which can result in poor spatial image and loss of tone. No other 3D technology can offer the user a "set-and-forget" feature like this.
Developed by Desper Products Inc, USA and widely used by the recording and entertainment industry (with credits such as Walt Disney's "The Lion King" movie/soundtrack) the 3D Spatializer technology has leaped from the consumer electronic markets of TV's and Hi-Fi's to the desktop computer, and is fast becoming the '3D' by which others follow.. " ESS website
ES1868 Cost Saver 3D 





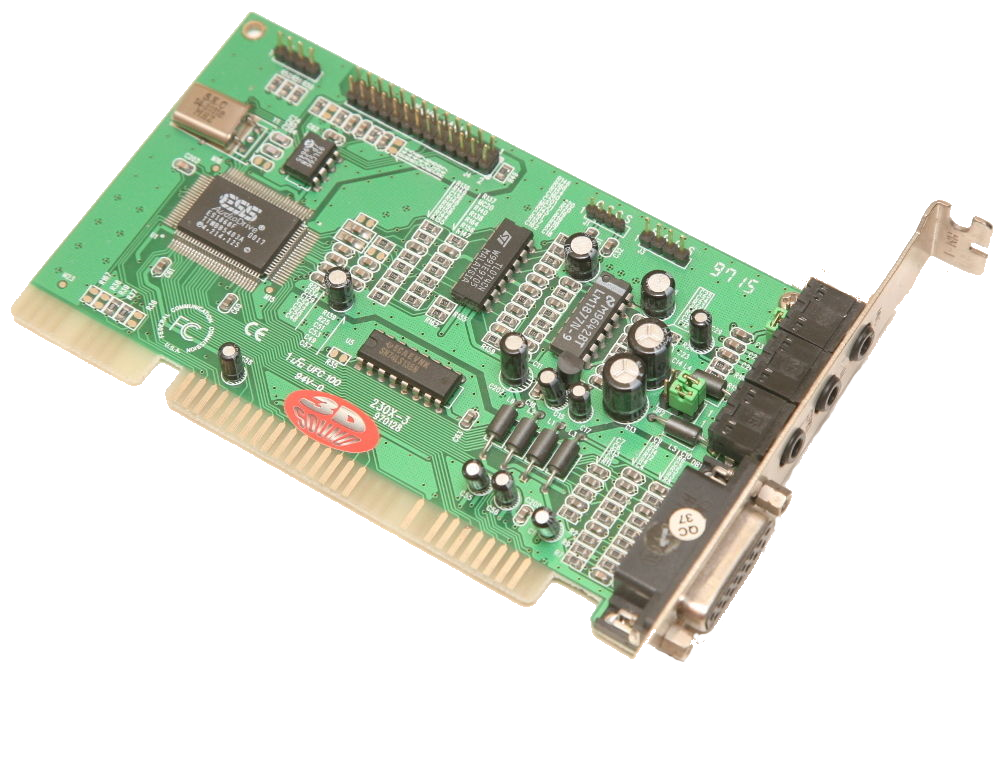
Introduced: 1996
Interface: 16-bit ISA
Chipset: ES1868
Plug & Play
Onboard "Binaura 3D" circuitry.
Wavetable header does not suffer from any bugs like SB card hanging notes bug.
This card was also sold as the Pine Schubert 3D (PT-230X).
Windows 3.1, NT 4.0, Windows 95
ES1869 AudioDrive 





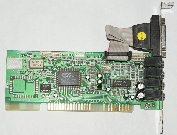
Introduced: October 1996
Interface: 16-bit ISA
Chipset: ES1869
OPL3 superset "ESFM" music synthesizer, IDE CD-ROM interface, dual joystick port, Hardware MPU-401 UART, "3D" spatial audio effects.
IDE interface for CD-ROM.
The ES1869 is a slightly upgraded version of the ES1868 chip. It supports the higher 48 kHz sample playback as well as 3D spatial audio.
Fremont, CA (October 2, 1996) --ESS Technology, Inc. (NASDAQ: ESST) today introduced three new audio devices to its existing AudioDrive family of products. These products, the ES1869, ES1887 and ES1879, address the separate needs of the three PC market segments (PC Motherboard, PC Add-in card and PC Notebook). The ES1869 and ES1879 comply with MICROSOFT PC 97 logo requirements, offering high fidelity audio, full duplex stereo, and support the emerging requirement for telegaming (games over modem).
These extensions of ESS Technology, Inc.'s AudioDrive family have many common features, including a single chip solution, 16 bit CD-quality, full duplex stereo sound, PC audio and games support in Sound Blaster® and Sound Blaster Pro® modes, high quality audio with ESS Technology, Inc.'s ESFM™ music synthesis and hardware volume control. These products support a broadside ISA bus interface, advanced power management modes, software addressable selections for Plug and Play (PnP), and feature glueless interfaces to various devices, including a MIDI synthesizer, DSP processor and external wavetable music synthesizer.
DESKTOP PC MOTHERBOARD AND PC ADD-IN CARD
The ES1869 applies to all three PC segments, but primarily addresses desktop PC motherboards and PC add-in cards. For the desktop PC motherboard, the ES1869 integrates 3D Spatialization, Enhanced Telegaming Architecture, and a new high fidelity analog front end. The 3D Spatializer audio produces a rich 3D soundstage from two stereo speakers, generating accurate placement of sounds with soundstage localization information.
For add-on card applications, the ES1869 provides support for PnP and an audio/telephony device interface. The PnP support includes up to seven internal logical devices and three external devices. The ES1869 interface to a fax/modem subsystem includes a synchronous DSP serial port to connect directly to a modem DSP and full duplex direct connect for speakerphone. The ES1869 runs in industry standard 100-pin PQFP and TQFP packages. Samples are scheduled to be available in November 1996, with volume production shipments in the first quarter of 1997.
The ES1887 is designed specifically for desktop motherboards, integrating an I2S interface to support the Zoomed Video Port specification for video and audio input to notebook PCs. The device includes the ESS Technology, Inc. Enhanced Telegaming Architecture which enables multiple-stream mixed audio playback of Wave, MIDI and FM synthesized audio, simultaneous with full-duplex voice over data (DSVD), all mixed and transmitted concurrently. The ES1887 also integrates a new 7 output/6 input Mixer Architecture with flexible data paths for playback and record. Supplied in a 100-pin PQFP package, the ES1887 is available now in volume production.
PC NOTEBOOK
The ES1879 has an architecture suited for PC notebook application and integrates 3D Spatialization, Enhanced Telegaming Architecture and a new high fidelity analog front end. The I2S interface supports Zoomed Video Port for video and audio input to PC notebooks. Extensive power management and a 6-wire interface to the company's current ES978 Expansion Audio Mixer product provide an integrated Notebook and Docking Station solution.
The ES1879 and ES978 constitute a two-chip set supporting multiple peripheral devices for Notebook and Docking Station connections. Also, this chip set supports "hot docking", eliminating the need to power off when docking the notebook. The ES1879's interface to a fax/modem subsystem includes a synchronous DSP serial port to connect directly a modem DSP and a full duplex channel for speakerphone. The ES1879 package is a slim-line 100 pin TQFP ideally suited to the PC notebook. Samples are scheduled to be available in January 1997, with volume production quantities shortly thereafter.
The matters discussed in this news release include certain forward looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties, including the timely availability and acceptance of new products, the impact of competitive products and pricing, the management of growth, and the other risks detailed from time to time in the SEC reports of ESS Technology, Inc., including the report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 1996. Actual results could differ materially from those projected in the forward looking statements. "
ESS website, 2nd October 1996
You can set the onboard jumpers to disable the onboard amplifier and you will get pretty decent output from this card. Suitable for 99% of DOS games.
If your ES1869 is embedded on your motherboard (rather than being on a sound card) and you are not getting music in your games, try disabling the audio in your BIOS and re-run ESSCFG to configure the card.
The card was also sold to OEMs such as:
- Compaq Premier Sound Audio Feature Board
- Compaq Business Wavetable (includes ES692S wavetable)
- Pine Technology PT233X
- Gallant Sound Conductor 16 PnP (FCC ID: KWX-SC202 W)
- (Unbranded card from China, FCC ID L6NS611)
- (Unbranded card that uses the ES1869FC)
- Daewoo YSBC-D261C (JC9261)
- BioStar M5SIB (embedded on mobo)
Drivers: DOS, Windows 3.1
ES1878 AudioDrive 





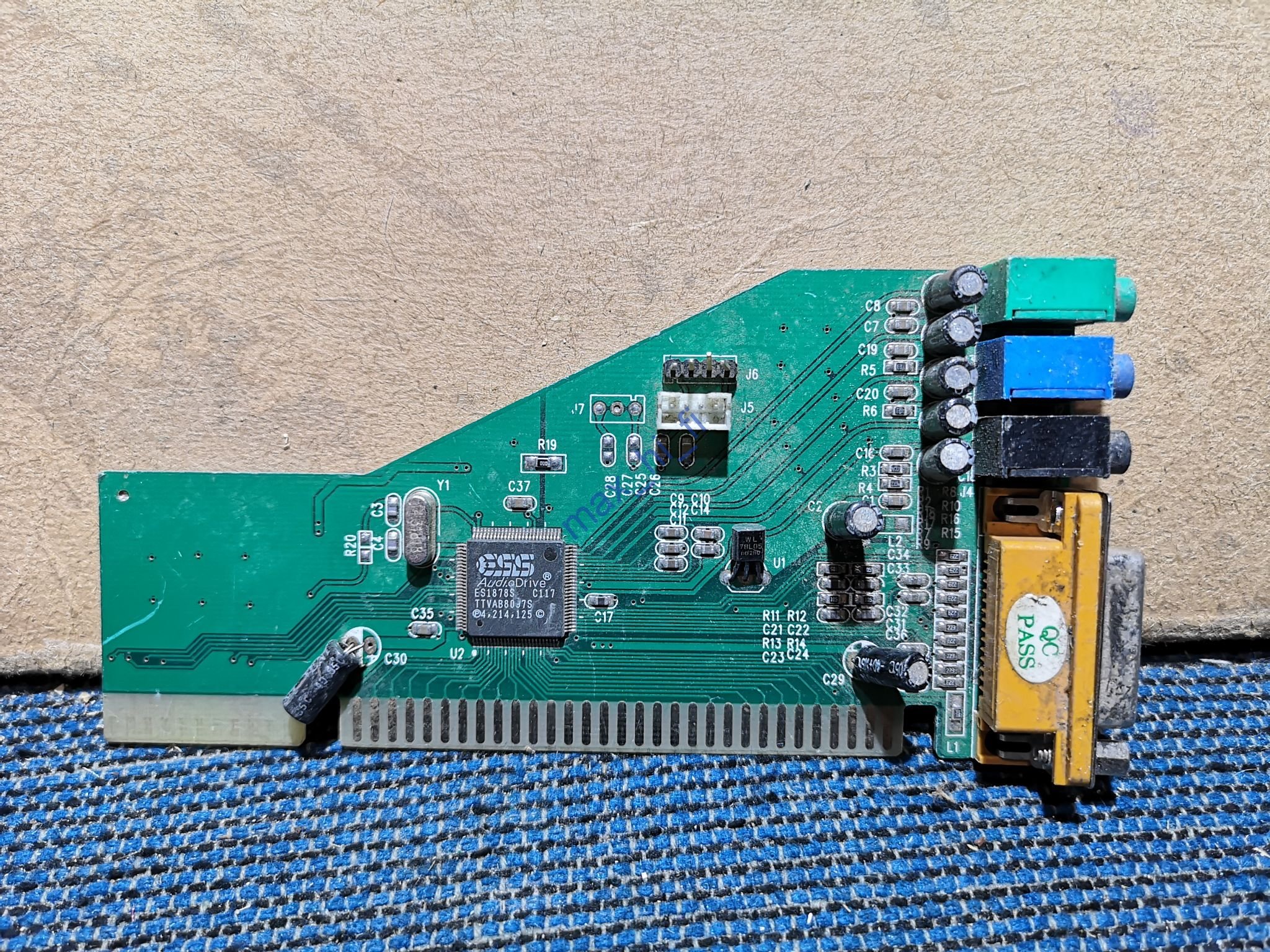
Introduced: ?
Interface: 16-bit ISA
Chipset: ES1878
PnP ISA sound card that uses the ESS ES1878S audio chip.
 ES1879 AudioDrive
ES1879 AudioDrive 





Introduced: October 1996
Interface: 16-bit ISA
Chipset: ES1879
Designed to be an embedded audio single-chip solution for Notebook computers. It supports ESS's ESFM OPL-3 compatible synthesis as well as Sound Blaster, Sound Blaster Pro and Windows Sound System.
It comes with an onboard ES938 3D effects processor from Spatializer, and allows connectivity to an ES689 or ES69x wavetable.
See the press release for this chipset in the ES1869 section.
 ES1887 AudioDrive
ES1887 AudioDrive 





Introduced: October 1996
Interface: 16-bit ISA
Chipset: ES1887
The ES1887 is pin-compatible with, and a superset of, the ES1888 AudioDrive® chip, adding improved configurability for Windows Plug and Play. The ES1887 is PC games compatible in SB and SB Pro modes and is compatible with Microsoft Windows Sound System. The ES1887 includes support for full-duplex operation, with simultaneous stereo record and playback using two DMA channels.
See the press release for this chipset in the ES1869 section.
 ES1888 AudioDrive
ES1888 AudioDrive 





Introduced: March 1995
Interface: 16-bit ISA
Chipset: ES1888
The ES1888 integrates digital logic and a microcontroller with audio CODEC and other analog functions onto one chip, and includes ESFM™ synthesis. The ES1888 is PC games compatible in SB and SB Pro modes and is compatible with Microsoft Windows Sound System. The ES1888 includes hardware volume control, 64 step volume control and dual game/joystick port for game support. The ES1888 also includes support for full-duplex operation, for simultaneous stereo record and playback using two DMA channels.
Fremont, CA (March 20, 1995) -- ESS Technology, Inc. introduced today the ES1888, the first integrated 16-bit stereo audio chip with on-chip music synthesis and Native Signal Processing support. The ES1888 supports PC audio and games in Sound Blaster™ and Sound Blaster™ Pro modes, and gains high-quality audio with ESS Technology, Inc.'s ESFM™ music synthesis.
Using the ES1888, system designers can implement sound card audio on a board design smaller than 1.5" x 2.0", adding audio capability to Multimedia PCs or notebook PCs; and designers gain support of Intel's Native Signal Processing (NSP) Native Audio with the ES1888 and its Native Audio MiniDevice software driver. The ES1888 provides all required circuitry for adding 16-bit stereo audio and 20-voice music synthesis to multimedia PCs, including 72-operator ESFM music synthesis. The ES1888 provides 16-bit stereo record and playback at sample rates of up to 44.1 KHz with CD-quality sound. The ES1888 has two independent analog mixers: a 7-channel playback mixer and 4-channel record mixer, with three stereo inputs for LINE-IN, CD-ROM, TV, plus one mono input for microphone.
Three stereo DACs support simultaneously three digital audio data streams: game, music synthesis, and host system playback. As specified in NSP, the ES1888 supports full duplex operation for simultaneous record and playback using two DMA channels, enabling full-duplex communications in applications including video teleconferencing and echo cancellation.
The ES1888 provides on-chip hardware compatibility for Sound Blaster™ games and DOS-based applications, maintaining compatibility with DOS software. The ES1888 and its associated NSP Native Audio driver enables Windows to schedule multiple applications to use the ES1888 hardware audio resource under NSP.
"The NSP architecture enables the full utilization of ESS Technology, Inc. Technology's AudioDrive® family capabilities," stated Albert Mak, Vice President of Marketing at ESS Technology, Inc. Technology, "including the ES1888's full-duplex simultaneous record and playback, and 72-operator ESFM music synthesis. The NSP structure provides a balanced architecture between Pentium processor software applications and audio accelerator functions."
"Within the NSP Native Audio architecture, Windows gains access to the resources of the ES1888 by controlling user application software requests," explained Bill Windsor, ESS Technology, Inc. Strategic Marketing Manager. "Signal processing software requests called MiniFilters are sent through the NSP Native Audio driver to the ES1888 MiniDevice driver, which is a Windows Ring0 32-bit Virtual Device Driver. This architecture under Windows provides real-time protected-mode control necessary for PC audio."
"ESS Technology, Inc. is demonstrating its NSP Native Audio driver this week at WinHEC'95," Windsor continued. "ESS Technology, Inc.'s NSP Driver for the full-duplex ES1888 AudioDrive will ship beta-qualified software at the end of April 1995." The ES1888 has special on-chip support for games functionality and control interfaces, including dual joystick interfaces and hardware volume control. The ES1888's three serial ports enable glueless interfaces to devices including a MIDI synthesizer, DSP processor, and external wavetable music synthesizer.
The ES1888 includes a broadside ISA bus interface, advanced power management modes for notebook PCs, and two software address selection modes for motherboard Plug and Play configuration. The ES1888 device driver and ES1888 Native Audio driver both support ESS Technology, Inc.'s high-quality ESFM music synthesis. "ESFM music synthesis is backward-compatible with FM synthesis, and provides superior sound quality with 72-operator ESFM music synthesis versus 36-operators for FM synthesis," said Albert Mak. "ESFM improves the depth and timbre of instrument sounds and enables chorusing of instruments. PC users with the ES1888 will immediately notice the difference in the depth and richness of computer music."
The ES1888 chip comes with device driver software that supports PC stereo audio under Microsoft® Windows™, Windows 95™, Windows for Workgroups™, Windows NT™, and Windows Sound System™ 2.0, in addition to IBM® OS/2 Warp™ operating systems. NSP Native Audio and the ES1888 MiniDevice Driver running under NSP are compatible with Windows™ 3.1 and Windows 95™. The ES1888 comes in a 100-pin PQFP and is sampling now.
The ES1888 is an extension of ESS Technology, Inc.'s AudioDrive family of audio chips, which includes the ES488, ES1488, ES688, ES1688, and ES968. List pricing for the ES1888 at OEM quantities is $28.00. ESS Technology, Inc., designs, develops and markets mixed-signal integrated circuits for speech, sound, and multimedia solutions for applications that range from PCs and instrumentation to consumer products. The company was founded in 1984, and holds 14 worldwide patents in time-domain audio compression and reconstruction technology. Since 1989, ESS Technology, Inc. has shipped over 70 million audio ICs."
ESS website, 20th March 1995
.jpg) ES1898 AudioDrive
ES1898 AudioDrive 





Introduced: 1997
Interface: 16-bit ISA
Believed to be a minor upgrade to the ES1869F and is 100% pin-compatible.
DOS Days contributor, Volodymyr Sharun, got in touch to say he bought a card '233X' that appeared to have a label on the main ESS chip indicating it was an ES1869F, but after removing the sticker discovered it was actually an ES1898F - the pictures here on his card.
Images
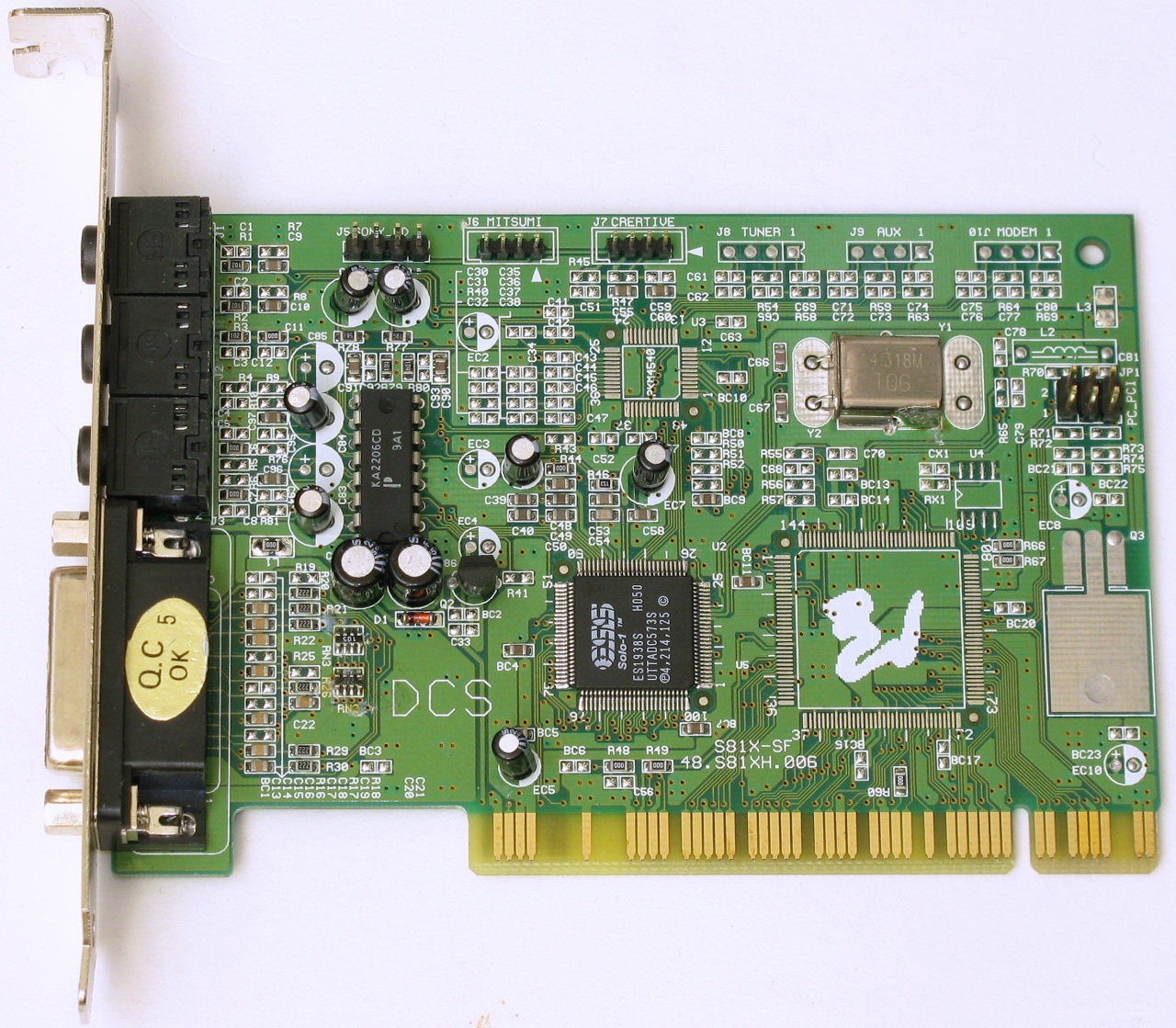
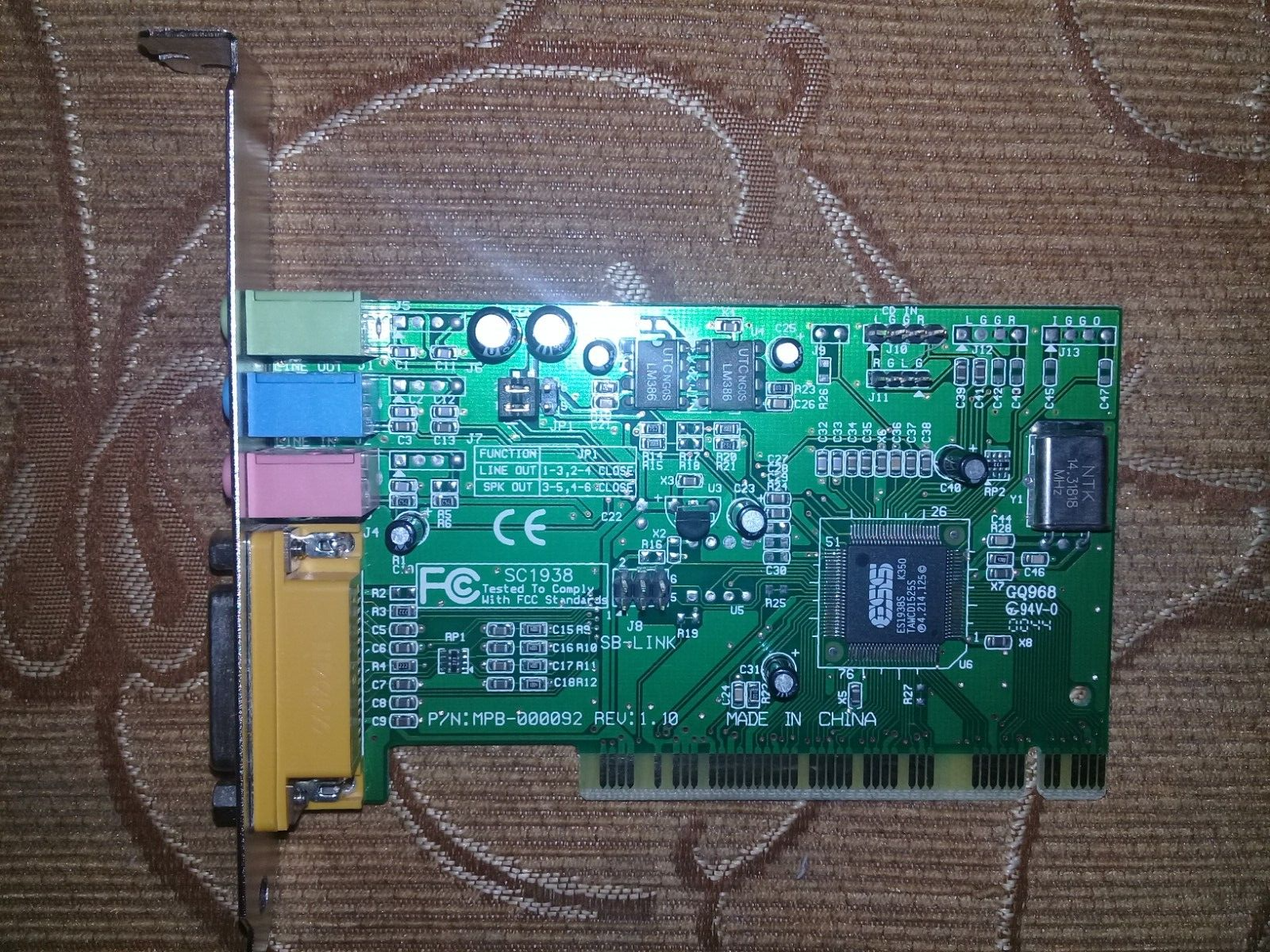
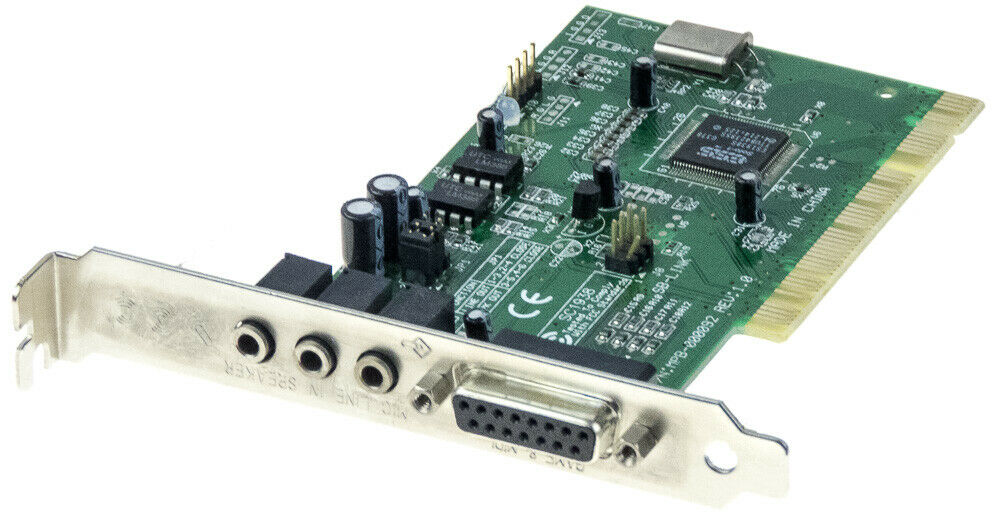
 ES1938 Solo 1
ES1938 Solo 1 





Introduced: 1997?
Interface: PCI
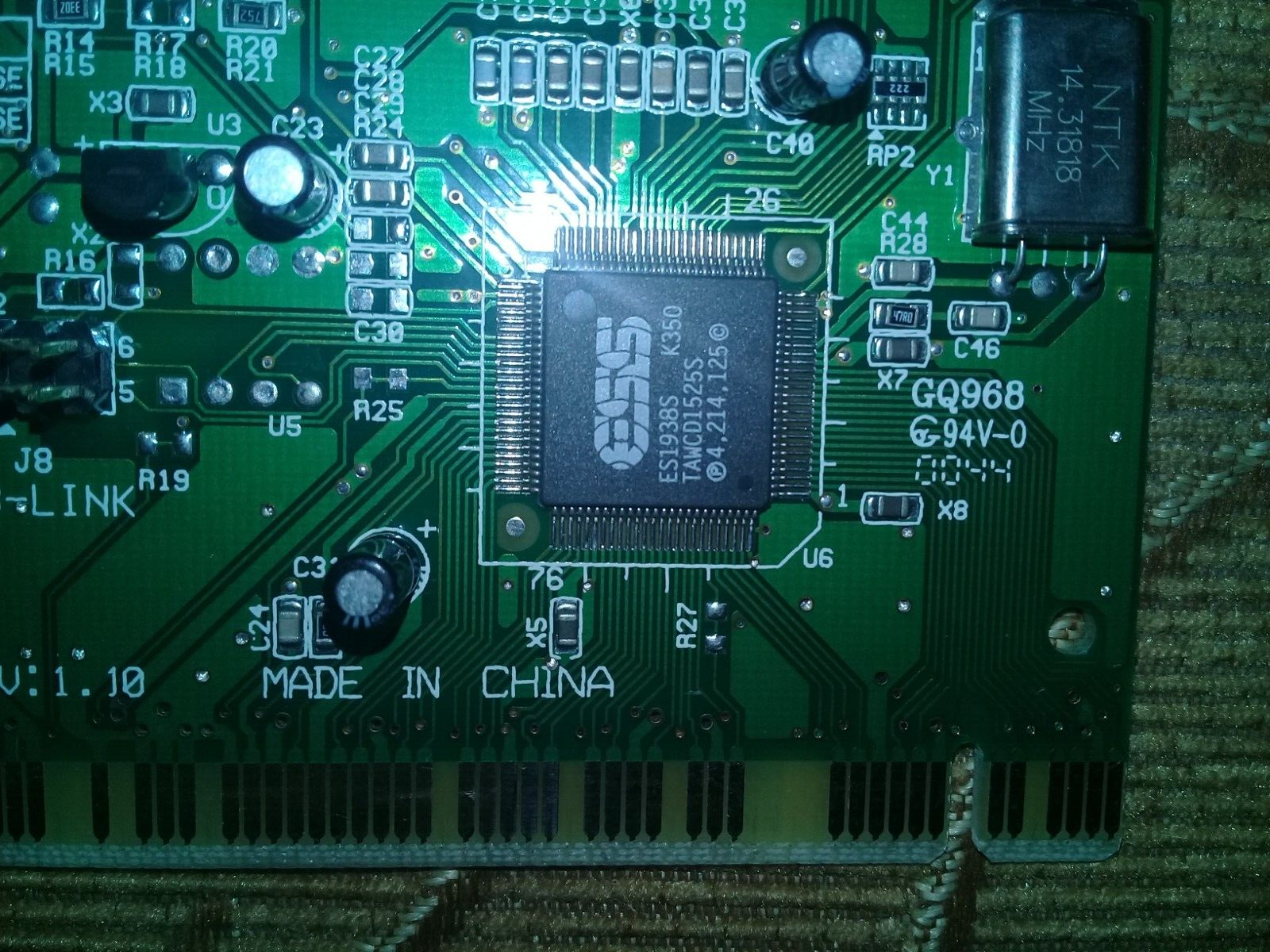
Chipset: ES1938
The ES1938 "Solo-1" was a PCI sound chipset made by ESS - the first in their PCI AudioDrive range.
The ES1938 incorporates a microcontroller, ESFM™ music synthesizer, 3-D stereo effects processor, 16-bit stereo wave ADC and DAC, 16-bit stereo music DAC, MPU-401 UART mode serial port, dual game port, hardware master volume control, a serial port interface to external wavetable music synthesizer, DMA control logic with FIFO, and PCI bus interface logic. There are three stereo inputs (typically line-in, CD audio, and auxiliary line) and a mono microphone input.
The ES1938 supported software-based wavetable audio and was DOS game compatible. The card featured an SB-Link header for connectivity to a supporting motherboard for DOS backward compatibility.
The chipset's signal-to-noise (SnR) ratio is poor. In playback [digital-to-analogue] tests conducted by PCAVTech, it got a Signal-to-Noise ratio of -64 dB.
The Solo-1 can be found on these cards:
- Terratec TTSOLO1-N
- Sertek DCS S819 / DCS S81X
- Formosa Sound Conductor (Part #: MPB-000092 Rev 1.0 and Rev 1.1)
- MultiWave AudioWave PCI Solo-1
It was also embedded on these motherboards:
- Chaintech 6ESA-2-E100N (Slot 1)
- ASUS ME-99 (Socket 370)
More Images
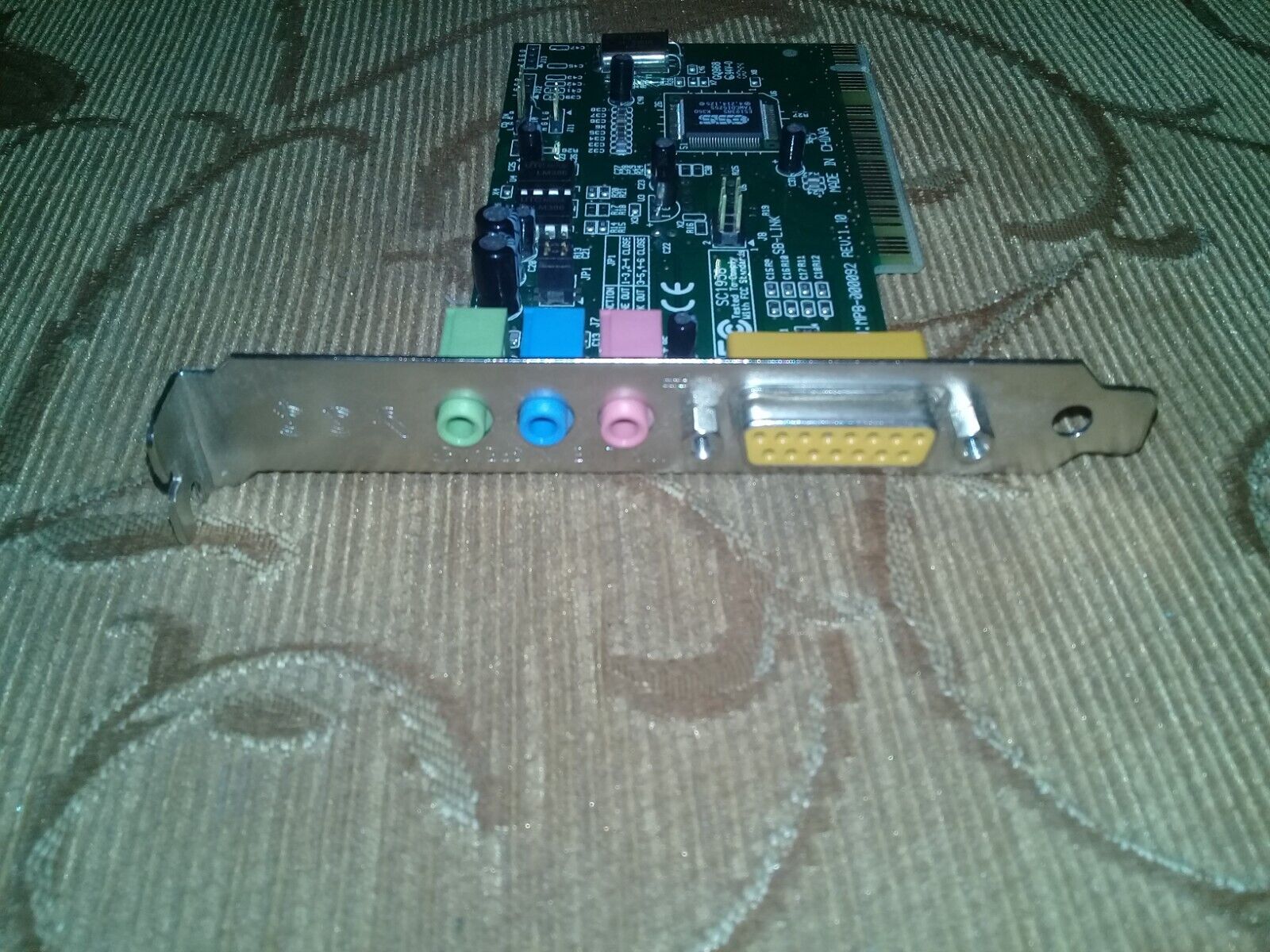





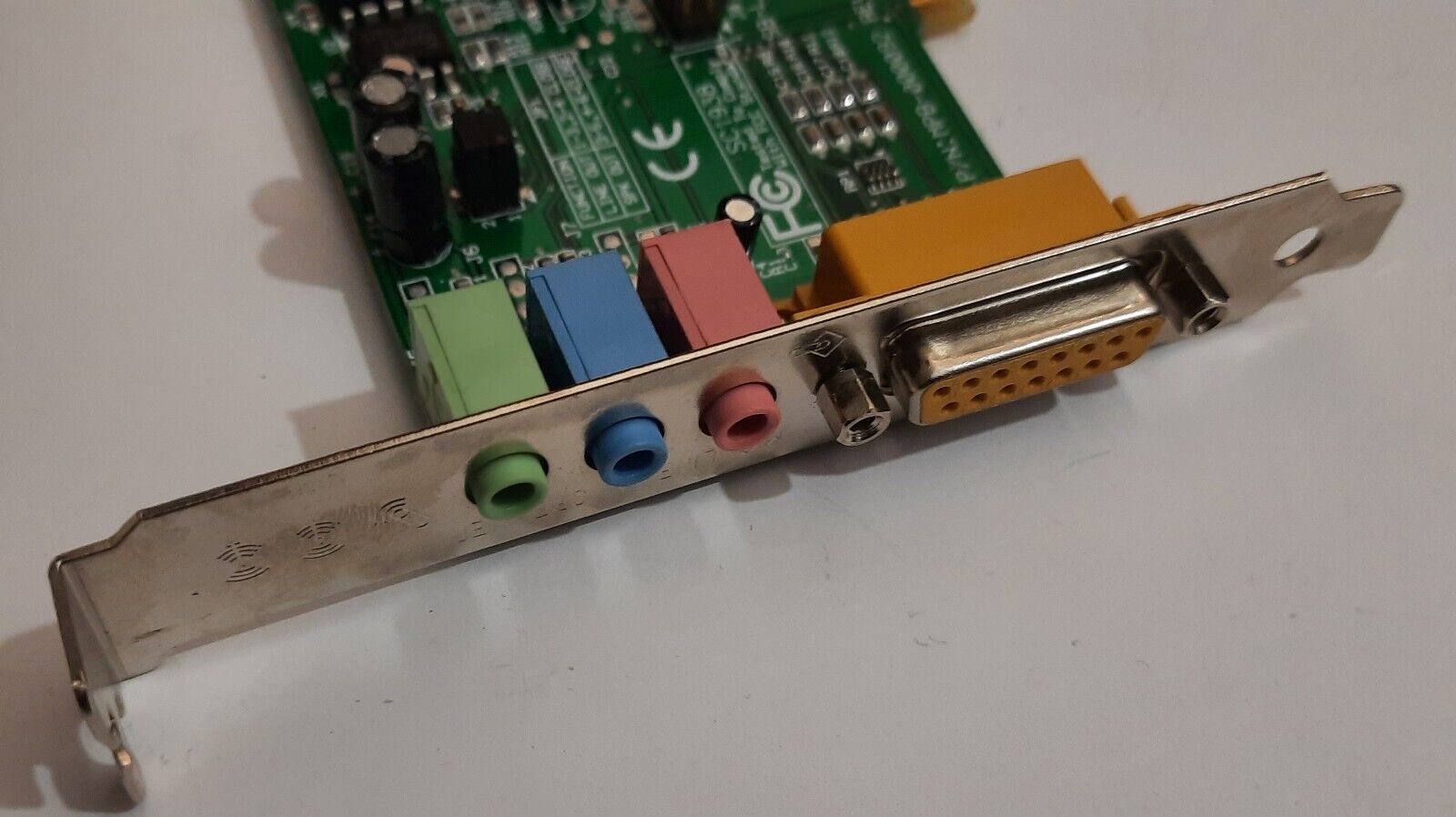
.jpg)
.jpg)
The above two images of a Terratec SOLO1-N are courtesy
of DOS Days' contributor, targeted.
 ES1946 Solo 1E
ES1946 Solo 1E 





Introduced: 1997?
Interface: PCI
Chipset: ES1946 Solo 1E
The ES1946 was also part of ESS' new PCI AudioDrive range.
The ES1946 PCI AudioDrive solution is a superset to the ES1938. It implements a single chip PCI audio solution providing high-quality audio processing with a dynamic range over 80db to comply with Microsoft® PC99 specifications and meet WHQL (Windows Hardware Quality Labs) audio requirements. The ES1946 is optimized to operate with 3.3 volt digital supply for notebook platforms.
The ES1946 incorporates a microcontroller, ESFM™ music synthesizer, 3-D stereo effects processor, 16-bit stereo wave ADC and DAC, 16-bit stereo music DAC, MPU-401 UART mode serial port, dual game port, hardware master volume control, a serial port interface to external wavetable music synthesizer, DMA control logic with FIFO, and PCI bus interface logic. There are three stereo inputs (typically line-in, CD audio, and auxiliary line) and a mono microphone input.
The ES1938 and ES1946 integrates ESS' field-proven hardware design for DOS game and compatibility with hardware FM synthesis (ESFM) and three methods for legacy audio control interface: PC/PCI, Distributed DMA, and Transparent DMA.
The ES1946 was used on IBM Thinkpad laptops around 1997. It provided compatibility for Sound Blaster, Sound Blaster Pro, and Windows Sound System.
More Images
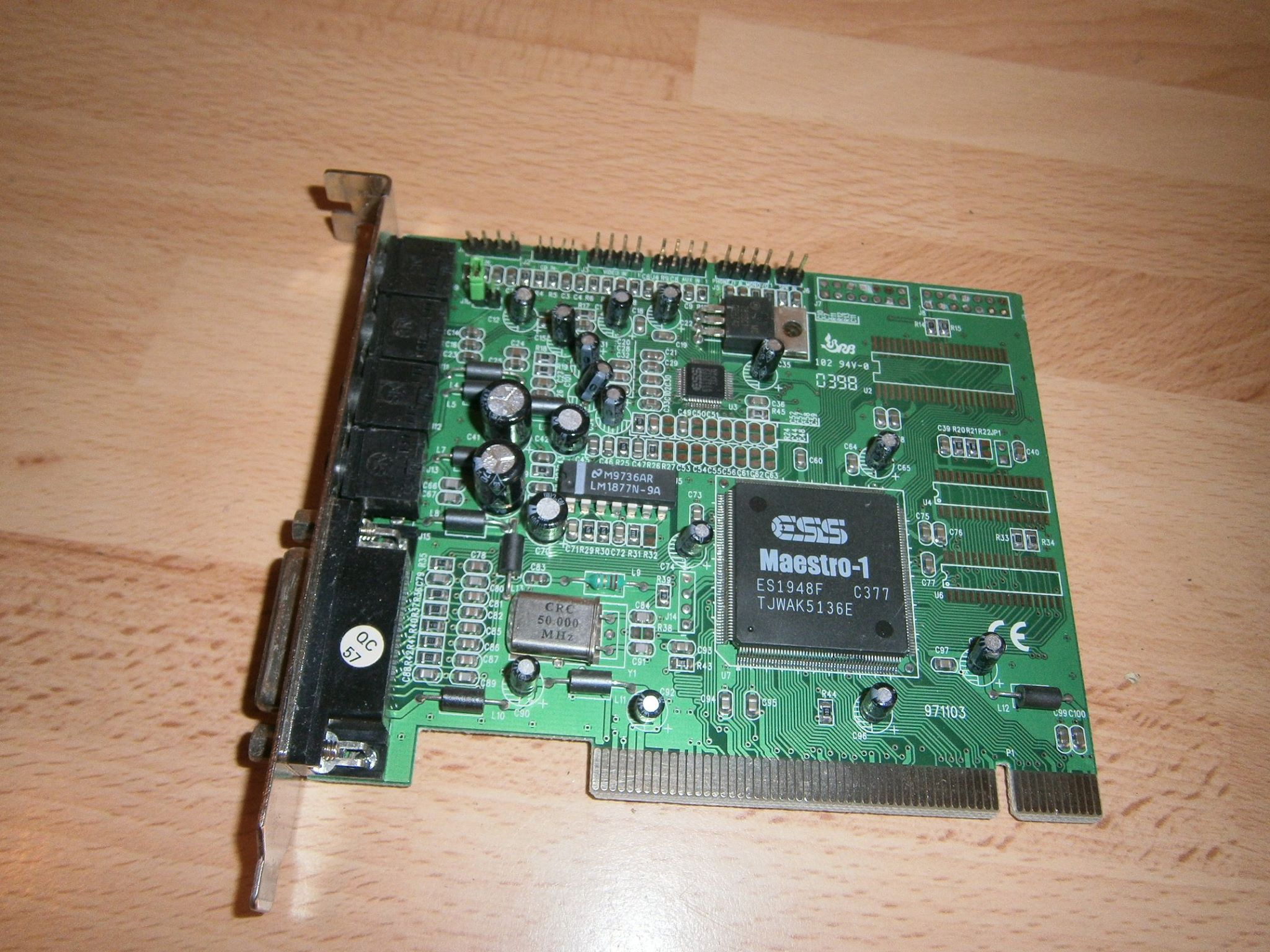
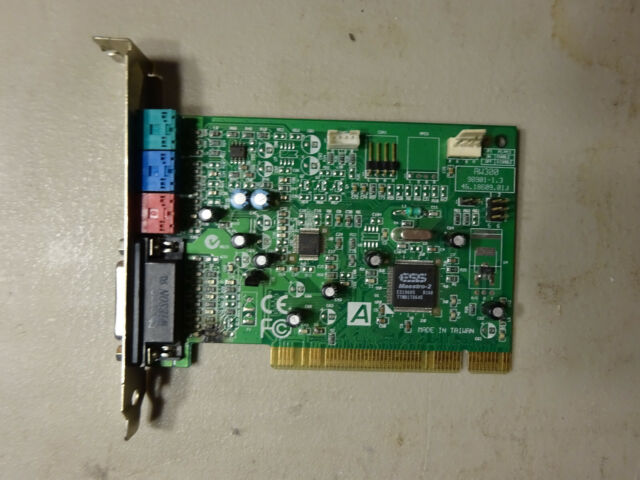
 ESS1948 Maestro-1, ES1968 Maestro-2, ES1978 Maestro-2E
ESS1948 Maestro-1, ES1968 Maestro-2, ES1978 Maestro-2E
Introduced: 1998
Interface: PCI
Chipset: ES1948F Maestro, ES1968F Maestro-2, ES1978 Maestro-2E
A PCI audio accelerator chipset with a 64-channel pipeline hardware Wave Processor and a proprietary audio signal processor. The Maestro PCI audio accelerators provided a high-performance PCI interface, while retaining compatibility to existing DOS games.
| Product Name | Maestro-1 | Maestro-2 | Maestro-2EM | Maestro-2E |
| DOS Game Compatible | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 32-bit PCI Bus Master System Interface PCI 2.1 Compliant | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Package | 208-pin PQFP | 100-pin TQFP | 144-pin TQFP | 100-pin TQFP |
| 3D Speaker Spreader | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Wavetable | Hardware | Hardware | Hardware | Hardware |
| Modem | No | No | Yes | No |
| PCI-to-PCI Bridge | Yes | No | No | No |
| Notebook Optimized | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Effect Synthesis | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Positional 3D | Q3D | Sensaura | Sensaura | Sensaura |
| Dual Game Port | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| DirectSound Acceleration | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| S/P DIF Output | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| AC97 Digital Docking | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| ES978 Docking | No | No | Yes | Yes |
All of the Maestro PCI audio accelerators comply with the Microsoft PC99 specification, AC'97 CODEC Interface, and PCI 2.1 Bus Specification.
Their architecture consists of a 64-channel pipeline hardware Wave Processor and a proprietary audio signal processor. Together they can simultaneously handle multiple audio streams of different data types, high quality MIDI synthesis, and voice compression and decompression. The synthesizer also performs advanced audio effects such as reverb, chorus, flange, echo and 3-D spatial enhancement.
The Maestro PCI audio accelerators provide a high-performance PCI interface, while retaining compatibility to existing DOS games with no restriction on system chipsets and no need for sideband signals. The PCI bus is required for PC audio hardware to smoothly reproduce high-fidelity audio from Internet, MIDI, wave, and conferencing sources. The PCI bus achieves high-performance functionality by enabling the transfer of multiple, independent data streams. PCI improves data transfer efficiency by at least 20 times over the ISA bus. This is crucial for low-latency audio applications, such as Internet interactive audio.
The MaestroPCI audio solutions accelerate Microsoft's DirectSound™ applications by digitally mixing more than 32 PCM streams of any frequency down to a single output stream of 48 kHz. This acceleration frees the CPU to perform other tasks.
The Maestro PCI audio accelerators support DOS game compatibility for both PC motherboard and add-in card solutions through three hardware implementations: PC/PCI, Distributed DMA (DDMA), and Transparent DMA (TDMA). While PC/PCI and DDMA are industry-standard protocols for legacy support, ESS' TDMA technology implements DOS game compatibility over the standard PCI 2.1 bus without the additional sideband signals.
The Maestro-2E PCI audio accelerator has two 20-bit AC'97 CODEC interfaces that can be enabled for notebook docking implementations. The secondary AC'97 CODEC interface can be programmed to handle multiple serial CODEC interfaces which, together with the primary AC'97 CODEC, can provide full-featured AC3 speaker outputs.
The Maestro PCI audio accelerators operate at 3.3 volts and have several special features for notebook operation. They are compliant with the Advanced Power Management (APM) 1.2, Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) 1.0, PCI Power Management Interface (PPMI) 1.0, and Intel's Mobile Power Guideline. They have multiple power-saving modes (D0, D1, D2 and D3) for power-efficiency when the audio system is both active and idle.
The Maestro-1's signal-to-noise (SnR) ratio is very poor. In playback [digital-to-analogue] tests conducted by PCAVTech, it got a Signal-to-Noise ratio of -62 dB. The Maestro-2's was much better at -74 dB which is considered good.
The Maestro-2 can be found on these cards:
- Diamond Sonic Impact S70
The ES1978MS was also used in a combination audio+modem device - in these uses, the "Maestro-2EM" is a combination of the ES1978 Maestro-2MS audio chipset and ES56CVM-PI modem in a single package
Maestro-1 datasheet
Maestro-2 datasheet
More Images
 ES1980 Maestro-3 / ES1983
ES1980 Maestro-3 / ES1983
Introduced: 2000?
Chipset: ESS ES1980, ES1980S or ES1983S
Interface: PCI
The Maestro-3i.COMM chipset was used in the Dell Latitude CPx J650GT notebook computer.
The ES1980 was also used in a combination audio+modem device - in these uses, the "Maestro-3i.COMM" is a combination of the ES1980 Maestro-3 audio chipset and ES56CVM-PI modem in a single package. Audio features include Sensaura™ HRTF positional 3D audio, multi-stream DirectSound and DirectSound 3D acceleration, and hardware SRC and digital mixing. In addition, it has the ESS SuperLink(TM) modem technology (first announced in May 2000), which ranked highest in connect speed and throughput when tested against other V.90 modem suppliers.
 ES1988 Allegro
ES1988 Allegro
Introduced: 1999
Chipset: ESS ES1988S
Interface: PCI
The ES1988 Allegro was also used on a combination PCI audio/modem device, comprising the ES1988 Allegro for audio and an ES56CVM-PI modem.
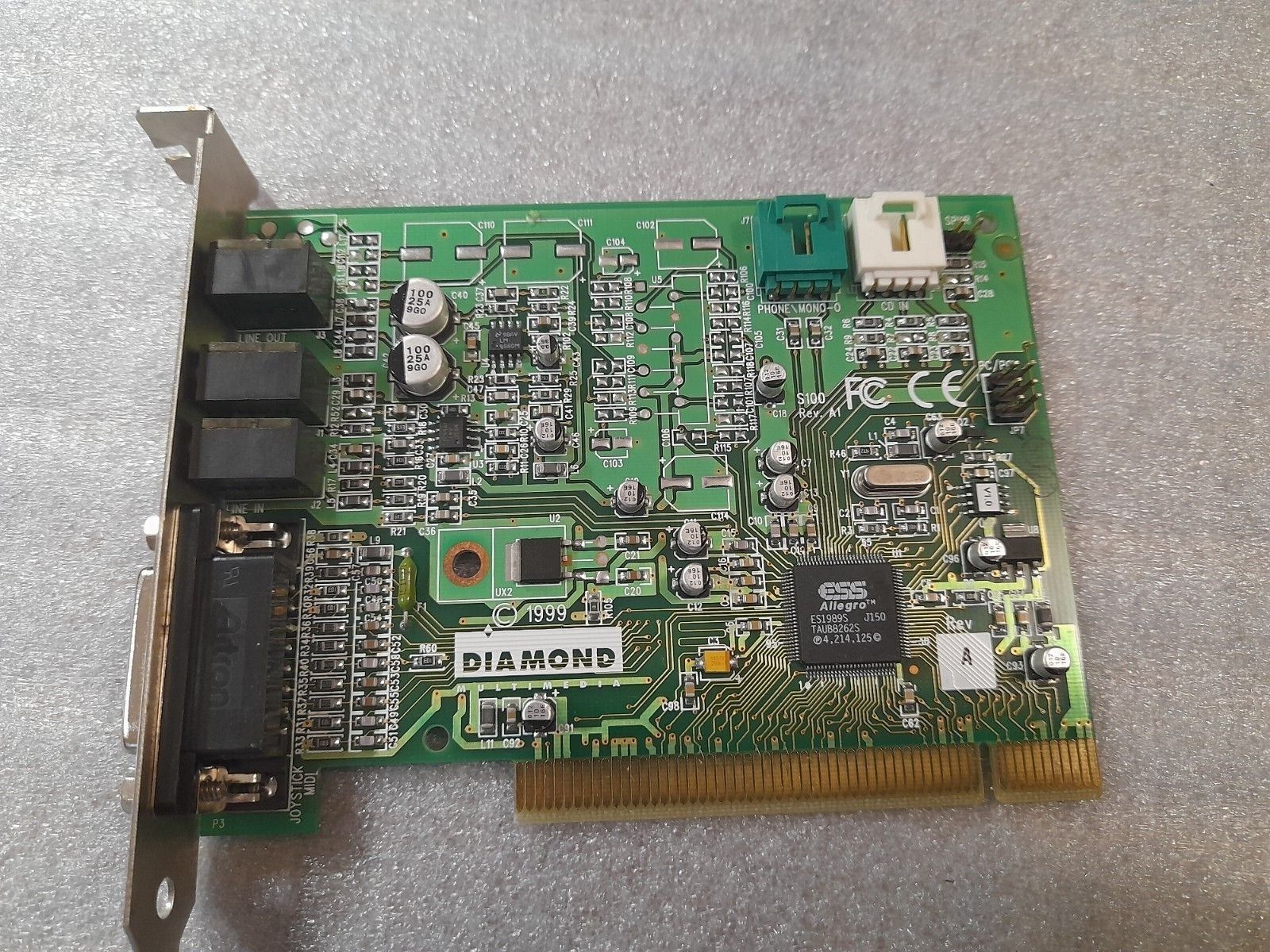
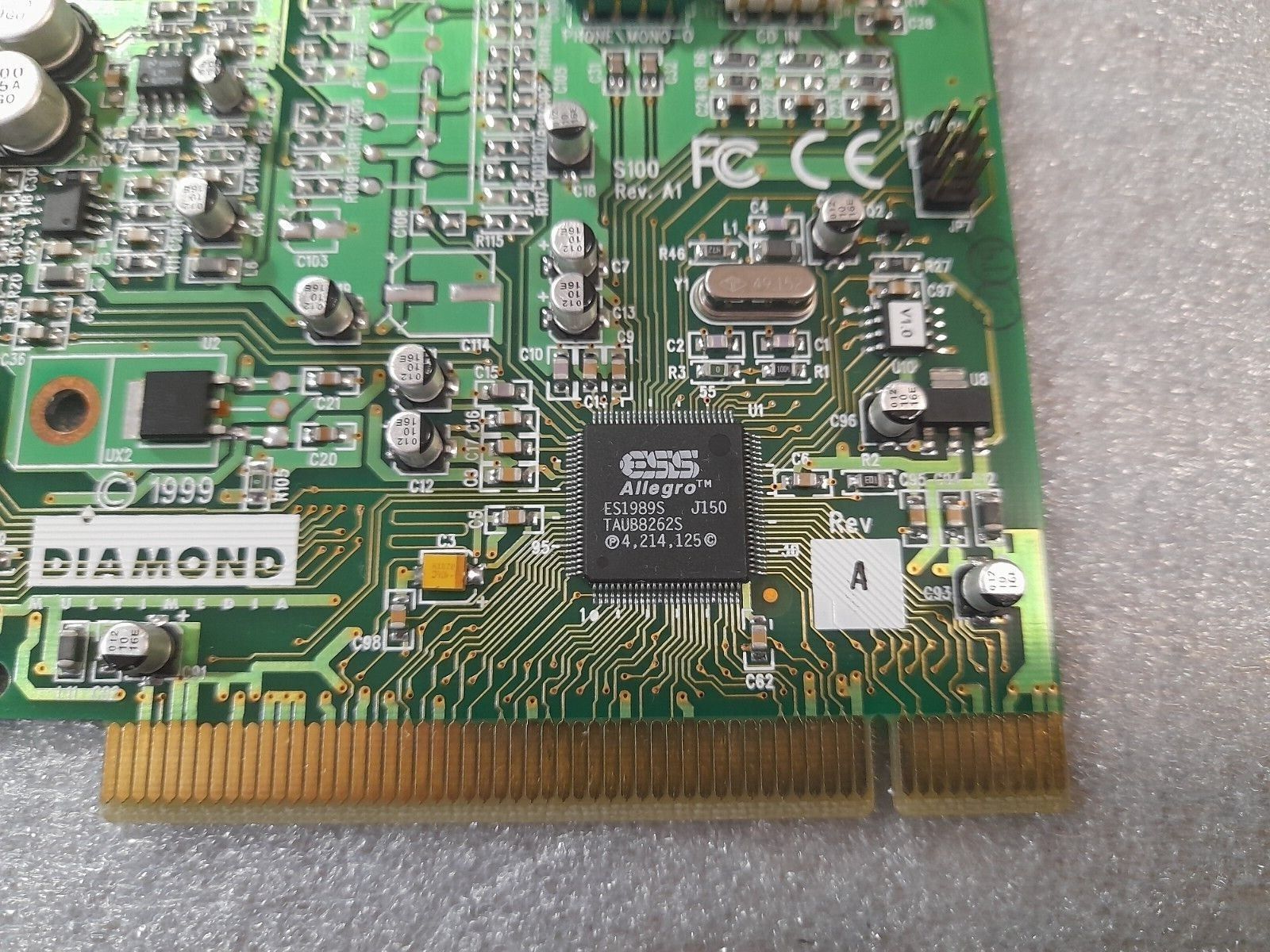
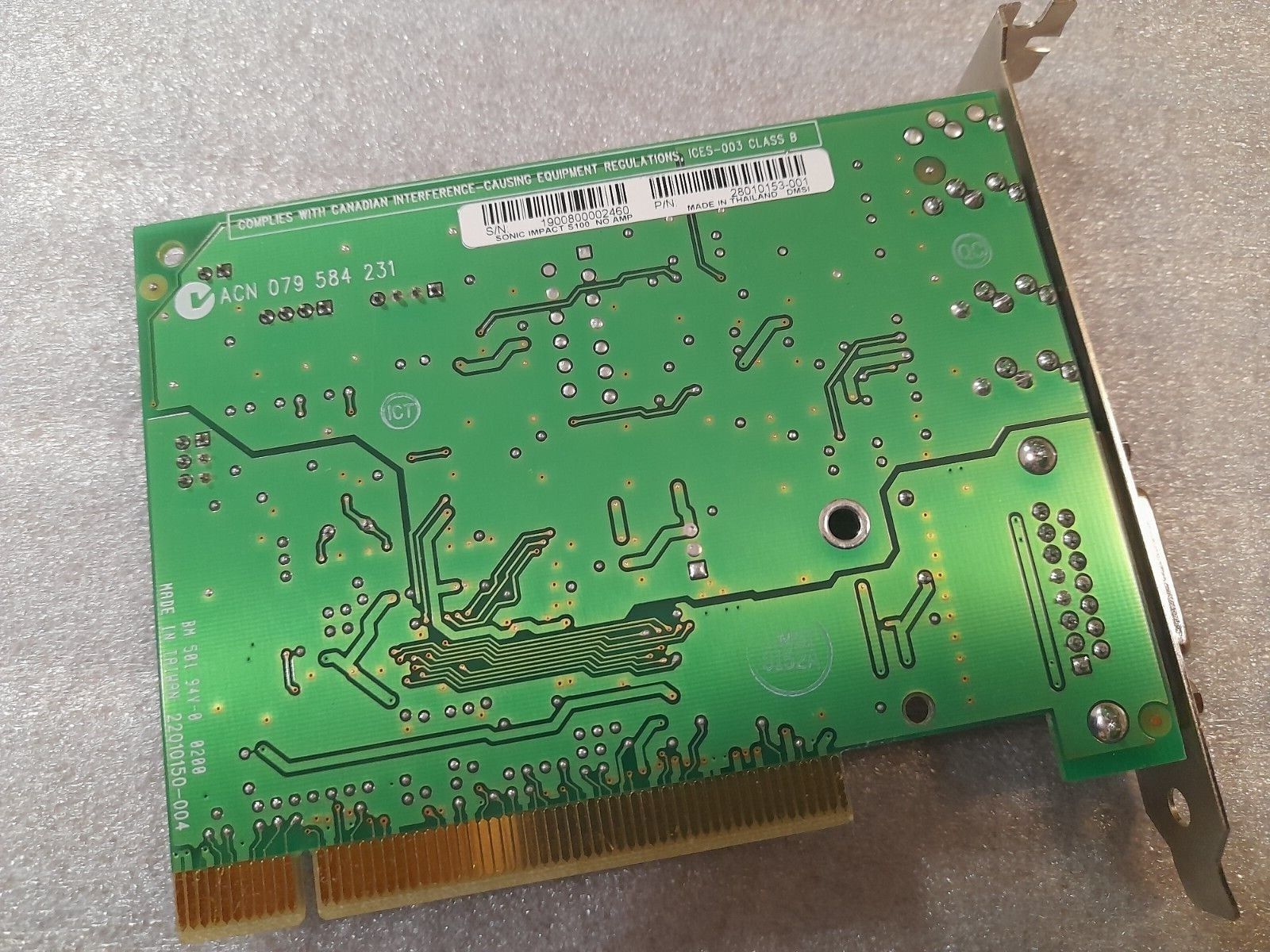
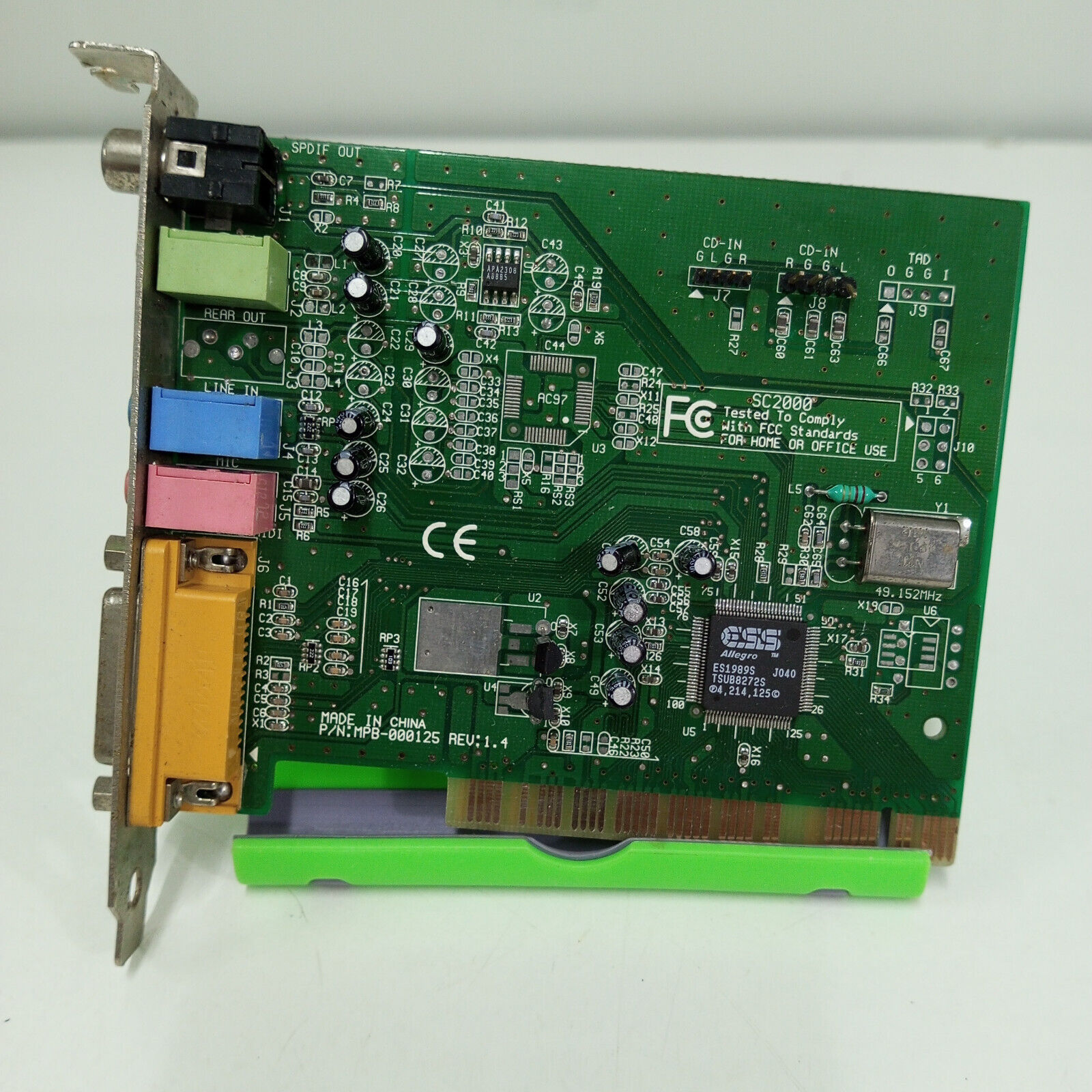
 ES1989 Allegro/ES1930
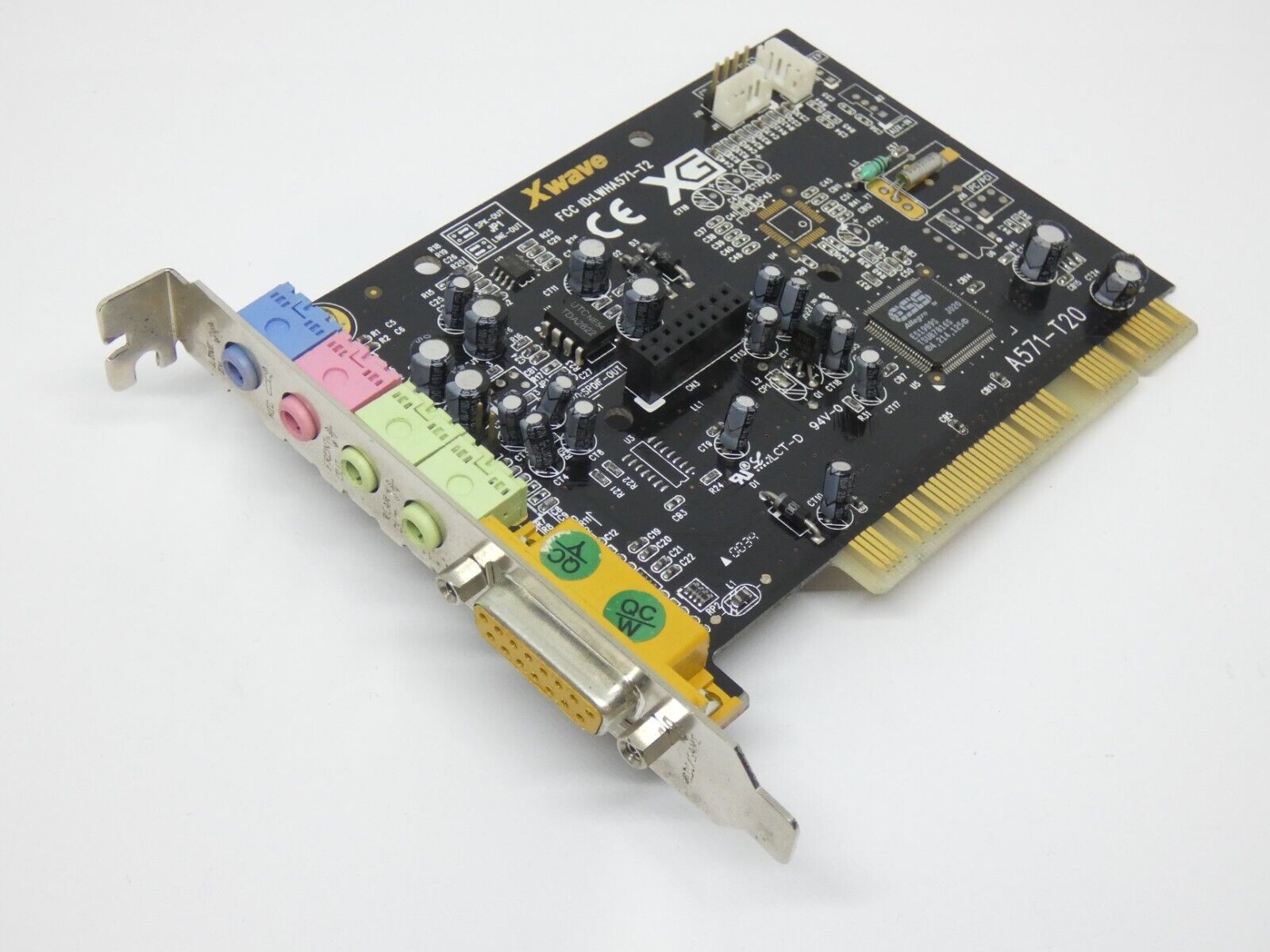
ES1989 Allegro/ES1930
Introduced: 1999
Chipset: ESS ES1989S
Interface: PCI
Some cards with Allegro chips also get an SB-LINK header. The Diamond Sonic Impact S100 is one.
This chip was used on the following cards:
- Diamond Multimedia Sonic Impact S100
- Labway Corporation XWave A571-T2 (FCC ID: LWHA571-T2)
- Formosa card (Part #MPB-00125 Rev 1.4)
- Pine Technology PT2635
More Images
 ES1970 / Canyon3D
ES1970 / Canyon3D
Introduced: 1999
Chipset: ESS ES1970S
The ES1970S Canyon3D audio processor contained ESS' proprietary Sensaura(TM) MultiDrive 3D positional audio, adding vertical positioning effects. It supported up to 6 speakers. Canyon3D rivalled Sound Blaster Live! and Aureal Vortex2 3D audio technologies.
From ESS' website in October 2000:
 A PC Gamer's Dream:
A PC Gamer's Dream: Canyon3D produces unmatched vertical positioning effects independently from all four speakers to exponentially enhance your PC gaming experience. Canyon3D(TM) is the world's first true positional 3D PCI audio accelerator designed for four speaker environments. The Canyon3D processor incorporates Sensaura's(TM) patented MultiDrive(TM) technology which produces vertical positioning effects. Other four speaker processors use simple 2D panning techniques to simulate a 3D world. Canyon3D allows you to identify an enemy's location based on sound effects, instead of relying on visual contact. Canyon3D technology provides the vertical audio cues needed for total game immersion. Canyon3D is the only accelerator to support four or two speaker environments with optional sub-woofers, as well as the popular 5.1 speaker configuration. Whether two, four or six speaker environments, Canyon3D creates the most realistic audio on the market. Experience "Adventures in Sound" from your classic DOS applications and from today's high-impact games with the Canyon3D audio accelerator. Proprietary hardware solutions from ESS enable Canyon3D to free the CPU's power for game processing and to provide complete legacy game support. Other audio processors rely on power from the CPU for software legacy support and 3D sound production. Canyon3D accelerates more than 32 DirectSound3D streams, while other processors handle only eight. Compatible with old and new game technology, Canyon3D allows you to experience the ultimate gaming environment without sacrificing support for your favorite DOS games.
Canyon3D: Sound Features
- Four speaker audio capabilities put you in the middle of the action
- World's first true positional 3D PCI audio accelerator
- Adds vertical positioning with Sensaura's patented MultiDrive technology
- Engulfing 4.0, 4.1 and 5.1 multi-speaker support
- Master balance/fade controls
- Individual Wave, MIDI and Analog controls
- Hardware solutions produce industry-leading real-mode DOS support
- AC '97 2.0 architecture
- Ultimate Dolby Digital and PCM support with S/PDIF digital output interface
- Microsoft DirectInput compatible joystick interface
- MPU-401 MIDI interface
- PCI 2.1 compatible interface
- Microsoft DirectSound and DirectMusic compatibility
Canyon3D(TM) Technology Backgrounder
INTRODUCTION
Today's PC is changing faster than ever before. As arcade-style gaming and theatre-quality surround sound become accessible to home users, unprecedented and potentially crippling demands can be placed on systems. ESS's new Canyon3D audio accelerator was designed to efficiently merge audio technologies into Microsoft® Windows® environments. With dual audio processing engines and flexible-streaming architecture, Canyon3D technology from ESS has raised the bar for 3D audio processors. Consumers have to consider many options when selecting an audio solution for a home PC. The audio solution must support today's demanding 3D games as well as home theatre environments. When supported with proper audio components, today's games produce a completely immersive 3D experience. The ability to play the latest DVD releases is also making PCs an integral part of home entertainment systems. From its unique support of true 3D gaming with Sensaura™'s MultiDrive™ technology to the unmatched speaker options for complete home theatre sound, Canyon3D is the ultimate in home PC audio.IMMERSIVE 3D GAMING
The release of DirectSound3D (DS3D) 5.0, Microsoft's industry standard API, introduced the PC gaming community to 3D positional audio. DS3D solutions are characterized by computationally-intensive algorithms that use Head Related Transfer Functions (HRTF) to encode natural hearing "cues" into the stereo audio stream. High-quality HRTF can produce sound sources in all three dimensions, which greatly enhances the enjoyment of 3D games. The first DS3D offerings were either too expensive or, in some cases, actually slower than the Microsoft's software emulation it replaced. With the introduction of the Maestro2 audio accelerator, ESS provided the first production-quality HRTF accelerator. The Maestro2 continues to set the standard for mainstream accelerators with unsurpassed acceleration and broad API support. CPU and graphic sub-systems enable more realistic visual environments. Game developers now offer audio that completes the 3D environment. By using environmental effects, like Microsoft DirectSound3D's Environmental Audio extensions (EAX), 3D games now have the capability to provide a completely immersive experience. Like graphics, not all systems support this leading-edge technology. In order to take advantage of new audio capabilities, an audio sub-system requires three things: acceleration of at least 32 DirectSound3D streams, quality HRTF 3D audio on at least four speakers and technology accessible through standard APIs.HOME THEATRE SOUNDAcceleration of at least 32 DirectSound3D streams: Many first generation "accelerators" require more than half the processing power of a PentiumII-400 to process 32 DS3D streams. Add environmental effects, and the load on the CPU greatly exceeds the 10% budgeted by most game developers. This can have disastrous effects, such as dropping audio sounds, jumpy graphics and game malfunctions. The Canyon3D processor accelerates more than 32 DS3D streams. This unsurpassed acceleration once again puts ESS's 3D audio accelerators at the front of the pack. Quality HRTF 3D audio on four speakers: Game enthusiasts are quickly adopting four speakers as the solution of choice. With its inherent reinforcement of subtle 3D audio cues and reinforcement of transaural crosstalk cancellation, four speakers provide the most immersive 3D audio experience. Unfortunately, a quality four-speaker environment cannot be achieved by simply adding an additional pair of speakers. In some cases, additional speakers actually diminish the 3D effects end-users desire. To date, three approaches exist to achieve a quality four-speaker gaming environment.The following chart summarizes 2nd-generation 3D audio devices:Technology accessible through multiple standards: ESS is committed to producing state-of-the-art audio technology. This means developing to industry standards. Canyon3D supports ALL popular programming interfaces: MS DOS® (Sound Blaster Pro), Windows® 95, Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0, Microsoft DirectSound®, DirectSound3D and derivatives including EAX. Unlike other devices that compromise silicon architecture for support of proprietary effects, Canyon3D enhances EXISTING games through standard APIs. An example is Sensaura's MacroFX™ which produces near-field proximity effects that offer a chilling new realism for 3D sound. By using existing information available in DS3D games, sounds closer than one meter, such as a whisper in the ear or an ultra-close "fly-by" from a bullet, are more realistic than ever before.
- Volume intensity panning. This Volume intensity processing does not fully utilize HRTF based algorithms. The result is little or no ability to change the elevation of sounds. Additionally, due to the Haas effect, without perfect speaker placement and balance, sounds quickly localize to a single speaker , creating jumpy transitions as an audio source moves from one location to another. While volume intensity panning does not burden the host CPU, it does create negative effects.
- Front positioning only. Front positioning solutions have HRTF-based 3D audio on the front pair of speaker and simple panning on the rear set. While sounds are in front of the listener, positional data does not suffer greatly. However, once objects begin to move to the side and then to the rear, the intensity panning problems mentioned above begin to affect the user's experience. While this solution does allow 1ST-generation processors to support 2ND-generation features, it sacrifices performance.
- Canyon3D. With its use of Sensaura's MultiDrive™ algorithm, Canyon3D is the only solution to play back true HRTF-processed data to ALL four speakers. Canyon3D uses this patented technology to produce vertical audio information, for any location in 3D space. Complete four-speaker processing diminishes the Haas effect, reducing the importance of speaker placement and balance control.
4.1 refers to four speakers plus a sub-woofer
Vortex 2 SB Live! Canyon3D DS3D streams 16 32 >32 Speaker configurations 2,4 2,4 2,4,4.1,5.1* 3D algorithm Front only HRTF Simple panning Sensaura MultiDrive Additional Effects Proprietary API Proprietary API Standard APIs
5.1 refers to four speakers plus a sub-woofer and center channel
The ability of a PC to play back DVD-encoded material is quickly becoming a necessary feature. DVD audio content is encoded in many ways. The most demanding format is AC3, a highly-compressed stream that carries the data required to drive a complete 5.1 channel (4 speakers plus a center channel and sub-woofer) speaker system. AC3 decoding and 5.1 channel reproduction are necessary to support Dolby Digital movies, THX, low frequency effects (LFE) and other sophisticated high-end home theatre features. Canyon3D's flexible internal architecture and processing power supports DVD playback in several ways, depending on the output configuration. The following chart summarizes output configurations and data playback.GLOSSARY
Output device Effect 2 Speakers Simple playback of front PCM data, or down-mixes the five channels of data using Sensaura 3D algorithm to 2 speakers 4 Speakers Playback of PCM data on front and rear stereo pairs data. Center data mixed to front speakers. 4.1 Speakers Playback of positional PCM data on front and rear stereo pairs data. Center data mixed to front speakers. Canyon3D digitally synthesizes LFE data. 5.1 Speakers All five channels sent to the appropriate speaker: Front left/right, Surround (rear) left/right , and Center. Canyon3D digitally synthesizes LFE data. S/PDIF AC3 stream sent to Dolby Digital receiver for decoding and playback via standard SP/DIF connection.
Interaural Cancellation - As a listener hears two speakers in the usual arrangement, each ear receives two signals. The right ear receives the intended direct sound from the right front speaker, plus the indirect signal from the left front speaker. Due to the difference in the distance from the source of the sound and the ear, the listener can identify the spatial location of the source, which can work against efforts to provide a virtual audio environment. Interaural cancellation works by minimizing the perception of indirect signals. In interaural cancellation, the audio signal is processed so that each channel has an interaural cancellation signal mixed with the main intended signal. The listener then receives pure right and left signals in the respective ears. With interaural cancellation, it is possible to produce a pseudo-binaural experience, much like wearing headphones, with little leakage or crosstalk between left and right channels. Interaural cancellation minimizes the user's ability to spatially locate the speakers, and can produce apparent sound sources outside the left speaker/right speaker/ listener triangle, up to 180 degrees (i.e. directly to the side of the listener's position). More sophisticated systems, such as HRTF, also cancel the effect of the listener's head transfer function on the sound to produce apparent sound sources from almost any point in space - above, below, behind, etc. Head Related Transfer Function (HRTF) - Algorithms that produce head related transfer functions produce audio through a filter that incorporates the effects of sounds reflecting off a listener's head, shoulders and outer ears. Input for HRTF-based 3D audio include the monaural sound source signal(s), the user position and orientation, and the position(s) of the sound source(s), while the output is projected in a multi-speaker environment. Haas Effect - The Haas (or "Precedence") effect[1], is the phenomenon that when presented with several similar pieces of audio information to process at slightly differing times, the brain uses the FIRST information to arrive from which to compute directional information, and then it attributes the subsequent, similar information packets with the same directional information. For example, if several loudspeakers were playing music at exactly the same loudness in a room, all the sound would appear to come from the nearest loudspeaker, and all the others would appear to be silent. The first signals to arrive are used to determine the spatial position of the sound source, and the subsequent signals simply make it sound louder. This effect is so strong that the intensity of the second signal could be up to 8 dB greater than the initial signal, and the brain would still use the first (but quieter) signal to decide from where the sound originated. This effect is known also as "law of the first wavefront", "auditory suppression effect", "first-arrival effect" and "threshold of extinction", and is used for the basis of sound reinforcement used in Public Address systems.1. Historical Background of the Haas and/or Precedence Effect, ,M B Gardner, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 43, (6), pp.1243-1248 (1968).
ES1992 Canyon3D-2 / ES1990
Introduced: 2001(?)
Chipset: ESS ES1990S or ES1992
I have no information on the Canyon 3D-2.


.JPG)


.jpg)