.jpg)
Floppy Disk Drives
Introduction
IBM released the first floppy disk drive in 1972 - these used 8" floppy disks. In 1976 the 5¼" floppy disk, the "minifloppy", was made available. The drives were manufactured by Shugart Associates initially, but by 1978 there were over 10 manufacturers producing 5¼" floppy drives in competing physical disk formats: hard-sectored (90 KB) and soft-sectored (110 KB). Before long, the hard-sectored format disappeared.
The first IBM PC was envisioned with a cassette tape, but typically it came with one or two 5¼" floppy disk drives. The idea behind having more than one drive was so that you could have your 'Program' disk in one (like a Word Processor application), and your 'Working Files' disk in another (where you stored your saved documents). In the earliest PCs these drives were "full-height", meaning they took up two drive bays - one on top of the other. In 1986 the IBM PC XT was made available which introduced the "half-height" drive which took up just one drive bay. This allowed the XT to have two floppy drives plus a full-height hard drive.


Physical Disk Geometry
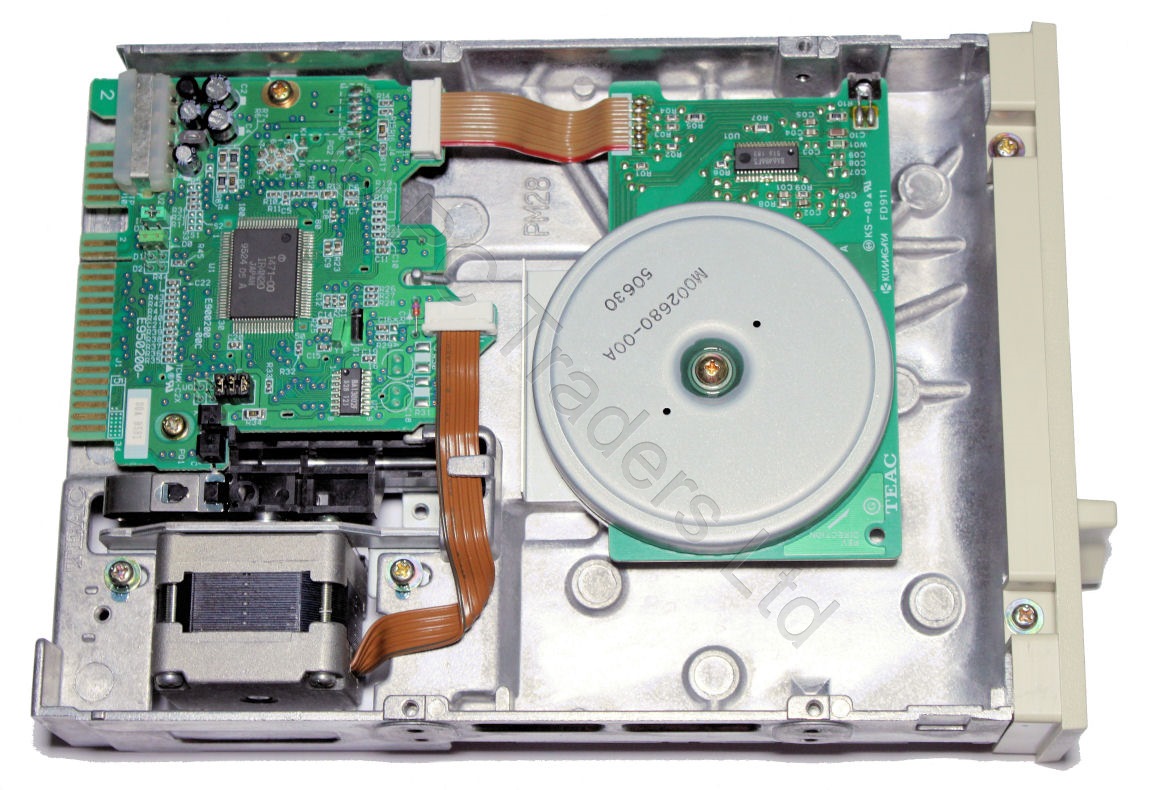
A floppy disk is essentially a very flexible piece (hence the term floppy disk) of plastic coated on both sides in a magnetic material. This 'disk' of plastic is contained within a protective envelope or hard plastic case, which is then inserted into the drive and automatically locked onto a spindle. It is then rotated at a constant speed (360 rpm for standard PC floppy drives) by means of a spindle motor. A head assembly consisting of two magnetic read/write heads, one in contact with the upper surface of the disk and one in contact with the lower surface of the disk, may be moved in discrete steps across the disk by means of a stepper motor.
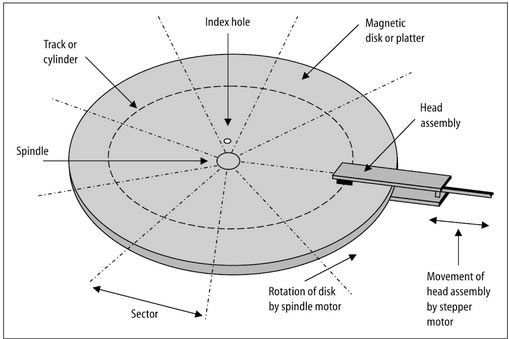
Due to the location of the head assembly and the fact the disk is spinning means the area of magnetic material that is passing under the upper head is seen to be a very narrow circular strip - this is called a track. Because there is both a track on the upper side of the disk and the lower side of the disk, both tracks together are called a cylinder. The number of possible cylinders for a given drive is clearly determined by the number of discrete steps available to the stepper motor. In practice, a track is considered too large a unit for storing information, so it is divided into sectors. Typically, each sector stores 512 bytes of data. The diagram above shows 9 sectors, which is typical of older 5¼" floppy disks. Later ones use 15 sectors per track, whilst the standard 3½" 1.44 MB floppy disk has 18 sectors per track. Cylinder numbers are the same as track numbers - they represent the position of the head assembly. The number of heads, tracks and sectors per track a drive has is called its geometry. If you multiply the number of heads by the number of tracks by the number of sectors per track a disk has, you will find how many sectors a given disk has. Multiplying that number by 512 will give you the total capacity in bytes.
For example:
A 5¼" double-sided low-density floppy disk has 9 sectors and 40 tracks per side, so 80 tracks in total if you count both the upper and lower side of the disk, so to calculate the total capacity:
9 x 80 = 720 [total sectors]
720 x 512 [bytes] = 368,640
368,640 / 1024 = 360 KB (kilobytes)
This same logic above works just as well for hard disks as it does for floppy disks, except a hard disk contains multiple heads, whereas a floppy drive has just one head.
Storage Capacities
 The first PC 5¼" floppy disks were single-sided, capable of storing 160 KB. In 1982 MS-DOS v1.1 added support for double-sided disks, increasing capacity to 320 KB (160 KB on each side). These disks allowed for 48 tracks per inch - after formatting they contained a total of 40 tracks with 8 sectors per track, and each sector could store 512 bytes. The formula for calculating disk capacity is:
The first PC 5¼" floppy disks were single-sided, capable of storing 160 KB. In 1982 MS-DOS v1.1 added support for double-sided disks, increasing capacity to 320 KB (160 KB on each side). These disks allowed for 48 tracks per inch - after formatting they contained a total of 40 tracks with 8 sectors per track, and each sector could store 512 bytes. The formula for calculating disk capacity is:
(bytes per sector) x (sectors per track) x (number of tracks)
e.g. 512 x 8 x 40 = 163,840 bytes (160 KB) x two sides = 320 KB
By 1983 and the introduction of DOS 2.0, support for 9 sectors per track arrived, which provided two more capacities: 180 KB (single-sided) and 360 KB (double-sided). Then, coinciding with the launch of the IBM PC/AT in 1984, came high-density disks which used 96 tracks per inch. This meant a formatted 5¼" floppy disk could now hold 1,200 KB (1.2 MB) of data. High-density drives could also read double-density floppy disks, which permitted owners of older media to be able to upgrade without concern. These new high-density drives in the IBM were typically the Y-E Data model YD-380. If a customer opted for a low-density drive with their AT, they would have Y-E Data model YD-580, which supported up to 360 KB disks.
Meanwhile, 3½" floppy disks, known as "microfloppy" and first invented by Sony, had been introduced in 1983. For the IBM PC world, these started off as single-sided double-density (SS/DD), which gave a formatted capacity of 360 KB - the same as a double-sided 5¼" floppy disk. Very soon after, double-sided double-density (DS/DD) 3½"disks were made available, giving a formatted capacity of 720 KB. In 1987, "high"-density 3.5" disks were introduced by IBM with the launch of their PS/2 Models 50, 60 and 80 which got a high-density 3.5" floppy drive - this doubled the 3.5" capacity to 1.44 MB.
In short, the following formats were commonplace in the PC world from 1983 to the early 2000s:
| Physical Size | Sides/Density | Formatted Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| 5¼" | Double-Sided, Double-Density (DS/DD) | 360 KB |
| 5¼" | Double-Sided, High-Density (DS/HD) | 1.2 MB |
| 3½" | Double-Sided, Double-Density (DS/DD) | 720 KB |
| 3½" | Double-Sided, High-Density (DS/HD) | 1.44 MB |
High-density floppy disks were so ubiquitous throughout the 80s and into the 90s partly due to the high relative cost of hard disk drives at the time - in 1989 the typical hard disk drive ranged from 20 MB up to 80 MB with an entry-level price point of £170 for 20 MB. This compared to 5¼" high-density floppies which sold in boxes of 10 for £14 (£1 per MB for floppy storage vs £8.50 per MB for a hard disk). In the U.S., prices were similar (1.56:1 exchange rate at the time) - a 20 MB hard disk drive went for $260 whilst a box of 10 floppies was $12.
The Floppy Drive Cable
The standard PC floppy drive cable has several connectors, usually either 3 or 5. The connector furthest away from the others connects to the 'host' (the motherboard header or your floppy disk controller header). There are then either 1 or 2 pairs of connectors - these are used to support either a 3.5" floppy drive or a 5.25" floppy drive. It is not advisable to use both connectors in a single pair - this is the reason for having the second pair.
You may also notice the cable has a "twist" before the last pair of connectors. This is used to determine which drive [in a multi-drive] system is drive 'A' or 'B' [also called drive '1' or '2']. From the pin out table below; the swapped pins determine the "floppy drive enabled" flag, and which drive motor is enabled. The pins are line 10, line 12, line 14, and line 16, while the other lines in the twist are ground lines.
This twisted cable idea came about as a convenience, as it meant PC builders didn't need to fiddle with the floppy drive jumpers for each customer's configuration. Back when floppy drives were prevalent, customers chose either a single or dual floppy drive, since hard disks were so expensive.
All floppy drives were factory-configured as Drive B: - any signals that went to the last pair of connectors (after the twist) got their signals reversed so the drive motor and 'floppy enable' signal would be interpreted as Drive A: due to the twist.
Here are the pinouts of the cable:
| -- | Host/Controller | Drive A | Drive B | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wire 1-9 | 1-9 | 1-9 | 1-9 | No Change |
| Wire 10 | 10 | 16 | 10 | Motor Enable Drive 0/1 |
| Wire 11 | 11 | 15 | 11 | Ground, No Change |
| Wire 12 | 12 | 14 | 12 | Drive Select 0/1 |
| Wire 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | Ground, No Change |
| Wire 14 | 14 | 12 | 14 | Drive Select 0/1 |
| Wire 15 | 15 | 11 | 15 | Ground, No Change |
| Wire 16 | 16 | 10 | 16 | Motor Enable Drive 0/1 |
| Wire 17-34 | 17-34 | 17-34 | 17-34 | No Change |
The 2.88 MB Floppy
A 2.88 MB floppy drive was developed by Toshiba (and manufactured by Mitsumi) in the late 1980s for IBM's new PS/2 range, but failed to catch on in large numbers outside of IBM. These drives employed a very tightly-packed 36 sectors per track, and required special "ED" (Extra Density) 2.88 MB disks to work. These look almost identical to high-density 3.5" floppy disks, but have an "ED" symbol and have their "media sensing" hole further down from the top-left corner than on a high-density disk - this allows 2.88 MB drives to recognise when ED media has been inserted.
One recognised contributing factor to this format not being widely accepted by other manufacturers is that the floppy disk controller needed to support a transfer speed of 1 Mbps (most could only cope with a maximum transfer speed of 256 Kbps on 720 KB drives and 500 Kbps on 1.44 MB drives). Since this meant a new controller card would be needed as well as the floppy drive itself, the cost of a PC manufacturer moving to the 2.88 MB floppy format was prohibitive.
IBM first fitted 2.88 MB floppy disk drives to their PS/2 Model 50, 60, 70 and 80 ranges. The drives had no separate power connector - instead the ribbon cable also supplied power to the drive. Some of these drives that were sold independently of an IBM PS/2 came with an adapter that converted the FDD interface from the proprietary IBM floppy interface to a standard 2-row 34-pin FDD connector and separate power connector. Even if your PC's BIOS supports 2.88 MB floppy drives, you still need this adapter for the drive to function.
3.5" Floppy Drives with 26-pin Connector
Some PC-compatible floppy drives used a 26-pin connector rather than the more commonly seen 34-pin one. Examples of this were the "combo" drives such as the Teac FD-505 that incorporated a 3.5" and 5.25" floppy drive in a single unit which were common in older Compaq PCs. Other examples are the Teac FD05 (used in a number of laptops/notebooks), Sony 0A-D30, and Citizen U1DA-38A found in the Amstrad 5286HD.
3.5" Floppy Drives with Edge Connector
Some early IBM PS/2s and other PCs had 3.5" floppy disk drives that had a 40-pin edge connector instead of the later 34-pin 2-row header. These include the PS/2 Model 50, 60, 70 and 80. These older drives require an adapter or special cable that converts its 40-pin edge connector to a 34-pin header.
These 40-pin edge connectors are NOT the same as those used by 5.25" floppy drives, as the IBM drives had their power supplied through this interface.
The make a cable that connects the 40-pin edge connector to a 34-pin header connector, use this diagram:
Cable to convert 40-pin edge connector to a 34-pin header connector:
*NC = Not Connected |
By 1993, PC compatibles were being sold with 3½" floppy drives made by the following manufacturers:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Y-E Data was a wholly owned subsidiary of the Yaskawa Electric Corporation, in Otsuka, Japan. Y-E Data Inc (YED) began in September 1973 and was one of the first Japanese businesses to venture into computer peripherals.
They saw IBM move from punched cards to floppy disk drives and imported technology from an American company called Orbis, Inc. Initially they simply resold the Orbis 8" single-sided drive domestically. It was capable of storing 128 KB on a disk. In 1974, they designed and produced their own floppy disk drive, the YD-74C - this was also an 8" single-sided drive.
It was followed in 1977 with an 8" double-sided drive, model YD-174. In 1978 their first 5.25" floppy drive was launched - model YD-274. Their first 3.5" drive would arrive much later in 1987 - the YD-800 series. The C-series was designed for portables. A later F-series arrived in 1989. These were 'slim', and had models YD-3042 and YD-3082. Y-E Data continued to produce floppy drives into the late 1990s when there was a shift to the USB interface for these drives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q) Can I get a 5.25" floppy drive connected via USB to a modern PC?
A) Yes! A company called Device Side Data have a product called the FD5025 USB 5.25" floppy controller. One great thing about this interface is that it works with not just PC drives, but also Apple, Commodore, Texas Instruments, Atari and more, and comes with Windows and Mac OS software to pull data off your disks for archival purposes! It costs $55 plus shipping within the USA.
There is also the Kryoflux which works a little differently. It's still an adapter but works at the lowest level of reading the magnetic flux from the disk, so it's agnostic of encoding scheme and spin speeds. It should therefore work with just about any format of disk. Software is included, and it's about 124 Euros.
If you want to try other ways... it's not particularly easy. What could be done is to find a 3.5" external floppy drive enclosure and use an adapter or modified cable similar to the one above on this page to convert its edge connector to a standard 34-pin 2-row header. The controller circuitry on the USB interface *may* support 5.25" drives (specifically 1.2 MB high-density ones), but it may not. Also, the HD (high-density) 5.25" drives run their motor at 360 rpm instead of the 300 rpm that all 3.5" drives spin at. SMSC made a USB bridge chip, USB97CFDC2-01. This supports "640K, 720K, 1.44M, 1.2M Windows 98 and 1.2M NEC DOS 6.x Formats" - you can possibly identify if your USB interface has this chip by checking in Device Manager. This chip has a VID of 0424 and a PID of 0fdc.
Power requirements are a little more tricky as many USB powered enclosures will not have enough power for a 5.25" drive. These usually have no more than +5V with a maximum current draw of 500mA. 5.25" floppy drives take power from a Molex 4-pin connector which provides +5V (red), GND (black), GND (black), and +12V (yellow). These drives do require both these voltage lines to function - the 12V line is used to power the stepper motor, and the 5V line is used for the logic board and read/write heads. So you'll need to get the +12V in there from a DC mains adapter.
Also be aware that PC floppy drives are jumpered as drive 1, not drive 0, so you will either have to find a cable with a twist, or determine how to re-jumper your drive.
Standard 5.25" floppy edge connector pinouts:
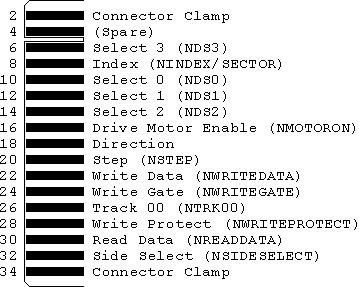
All pins on the other side are ground.






















.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

/images/tandon_tm-100-1A.jpg)
/images/tandon_tm-100-2A.jpg)